Fig. 1.
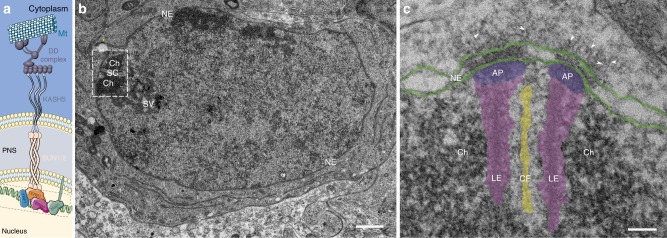
Transmission electron micrographs of murine telomere attachment sites to the nuclear envelope. a Schematic depiction of the molecular composition of meiotic telomere attachment sites. Telomere chromatin, which is bound by the meiotic telomere proteins (TRF1, TERB1/2, and Majin46), that are likely part of the attachment plate. LINC complexes anchored in the inner nuclear membrane that consist of the hetero-hexameric complex of inner nuclear membrane protein SUN1/2 and outer nuclear membrane protein KASH5 are depicted. KASH5 binds to the dynein–dynactin complex, which runs on microtubules. b Ultrathin section of a pachytene spermatocyte showing telomere chromatin (Ch) of the homologous chromosomes associated with the synaptonemal complex (SC) at the nuclear envelope (NE). c Telomere attachment site of epoxy-embedded frozen testis section. Lateral elements (LE, magenta) and central element (CE, yellow) of the synaptonemal complex, attachment plates (AP, purple), and nuclear envelope (NE, green) are highlighted. Arrowheads point at filaments originating from the inner nuclear membrane, spanning the perinuclear space and protruding into the cytoplasm. Scale bars (b, c): 100 nm