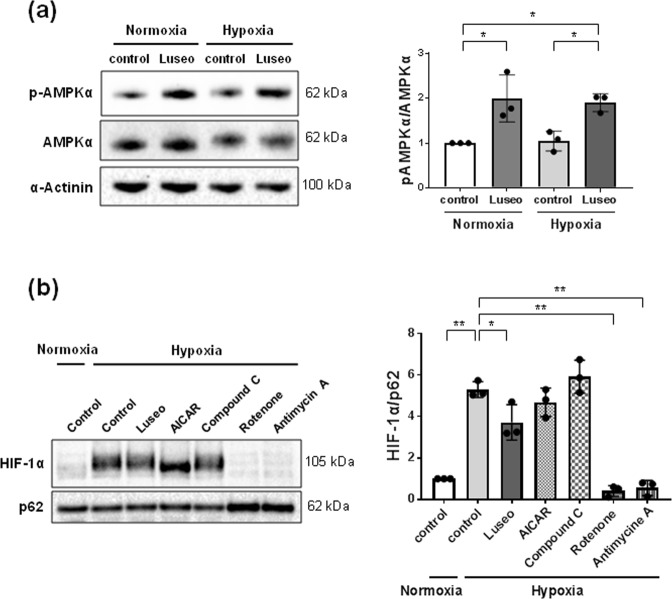
Figure 2.
Luseogliflozin inhibits the hypoxia-induced HIF-1α protein, independent of AMPK activation. (a) Protein levels of pAMPKα were determined by western blot analysis and quantitated by densitometry (n = 3). HRPTECs were treated with 100 μmol/l luseogliflozin under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 24 h. Then, total cellular extracts from HRPTECs were analyzed by western blot analysis and quantified by densitometry, with α-actinin as the loading control (n = 3). Luseogliflozin promoted the phosphorylation of AMPK under normoxia and hypoxia. (b) The inhibitors of mitochondrial respiratory complexes I and III, but not the AMPK activator and inhibitor, inhibited hypoxia-induced HIF-1α accumulation in HRPTECs. HRPTECs were treated with AICAR (1 mmol/l), compound C (20 µmol/l), rotenone (1 μmol/l) and antimycin A (10 ng/mL) under hypoxic conditions for 24 h. Nuclear extracts from HRPTECs were analyzed by western blot analysis and quantified by densitometry, with p62 as the loading control (n = 3). All results are shown as the means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.