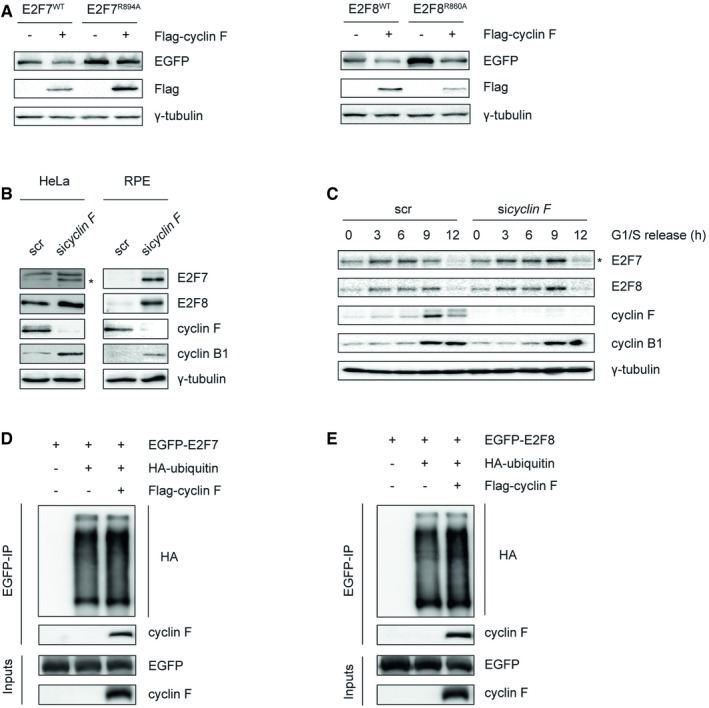
Figure 3. E2F7 and E2F8 are targeted for ubiquitination and degradation by cyclin F during G2/M.
-
AWild‐type or mutant versions of EGFP‐tagged E2F7/8 were co‐transfected with either empty vector or Flag‐tagged cyclin F in HEK293 cells. Nocodazole was added to cells 8 h before harvest. Forty‐eight hours after transfection, cells were collected and lysed for immunoblotting.
-
BKnockdown of cyclin F stabilized E2F7 and E2F8. HeLa and RPE cells were transfected with either scramble siRNA or pool cyclin F siRNA. Cells were harvested at 48 h post‐transfection. Protein levels of E2F7/8 were analyzed by immunoblotting. Asterisk indicates the specific band of E2F7 detection.
-
CCyclin F targets atypical E2Fs during G2/M. HeLa cells were transfected with either scrambled siRNA (scr) or cyclin F siRNA (sicyclin F) for 24 h. Then, cells were synchronized by double thymidine block and released into fresh medium after the second block. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points after the release. Protein expression was measured by immunoblotting, and cell cycle progression was determined by flow cytometry (shown in Fig EV1A). Asterisk indicates the specific detection of endogenous E2F7.
-
D, ECyclin F contributes to the ubiquitination of E2F7 and E2F8 in vivo. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA‐E2F7/8, with or without Flag‐cyclin F, and with HA‐tagged ubiquitin. Five hours before harvest, cells were treated with MG132. Forty‐eight hours after transfection, HEK cells were harvested and lysed for immunoprecipitation pull‐down assay with anti‐HA resin followed by immunoblotting.
Source data are available online for this figure.
