Figure 4.
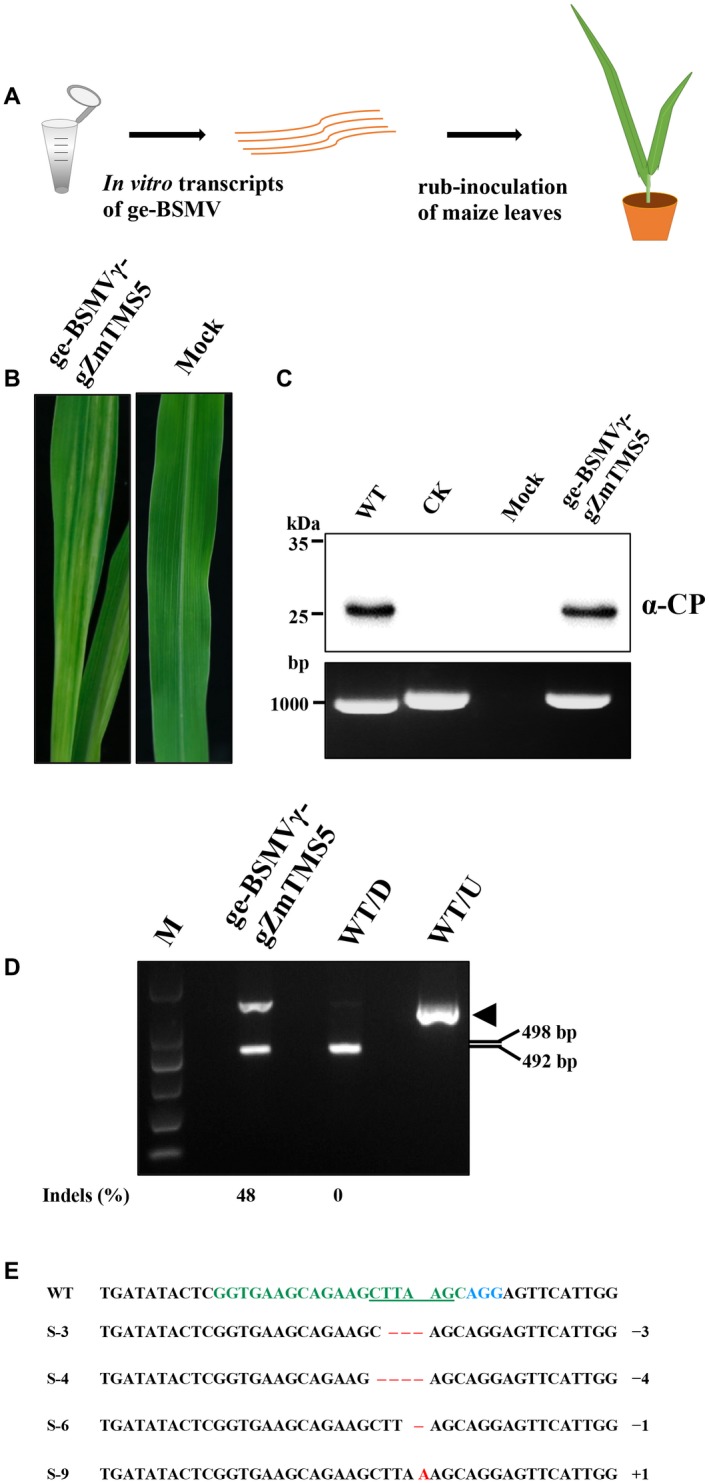
BSMV‐mediated targeted mutagenesis of ZmTMS5 in maize. (A) Workflow of ge‐BSMV‐mediated targeted gene editing in maize. In vitro‐transcripts of pT7‐αXJ, pT7‐βXJ and pT7‐γ‐gZmTMS5 were rub‐inoculated onto Cas9‐transgenic maize seedlings at the two‐leaf stage. (B) Symptoms of maize infected with ge‐BSMVγ‐gZmTMS5. Controls were FES buffer‐inoculated maize (Mock). (C) Western blot and RT‐PCR analysis of ge‐BSMVγ‐gZmTMS5 infection in the systemically infected maize leaves. Sample names are indicated above the panels. Antibodies used for western blots are indicated at the right of the panel. The molecular weight size markers in kDa or the sizes of DNA fragments in bp are indicated at the left side of each panel. WT, wild‐type BSMV‐infected maize leaves; CK, the pT7‐γ‐gZmTMS5 plasmid was used as a positive control for evaluating the size of the RT‐PCR products. The protein loading buffer alone was used as a control in western blot analyses. (D) PCR/restriction enzyme analysis of ge‐BSMVγ‐mediated genome editing of ZmTMS5 in systemically infected maize leaves at 24 days post‐inoculation (dpi). DNA fragments flanking the target site were amplified and subjected to AflII digestion. The arrowhead indicates the AflII‐resistant band (Note: due to size similarities, two of the digested DNA fragments appeared as one band in the gel). Mutation frequencies [indels (%)] were calculated by measuring band intensities with ImageJ software (v. 1.51k) and are shown below the corresponding lanes. WT/D and WT/U, DNA fragments amplified from wild‐type BSMV‐infected maize plants were digested (D) or not digested (U) with AflII. (E) Sanger sequencing analysis of the ZmTMS5 target site in DNA of leaf samples infected with ge‐BSMVγ‐gZmTMS5 at 24 dpi. The protospacer is shown in green, the PAM (NGG) motif is in blue, underlined nucleotides indicate the AflII recognition site, indels are shown in red with the dots indicating deleted nucleotides and red letters specifying inserted nucleotides. The numbers on the right indicate how many nucleotides were deleted (−) or inserted (+) in the ZmTMS5 target site by BSMV‐mediated genome editing.
