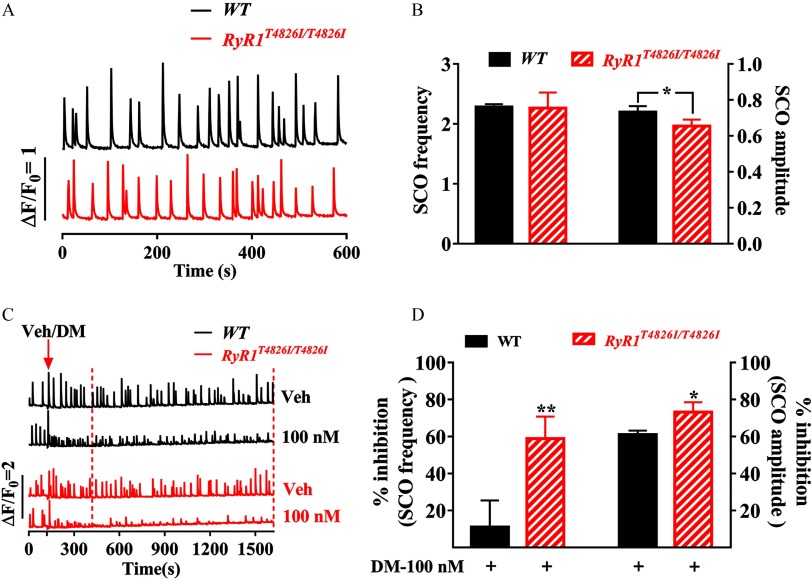
Figure 8.
Impacts of mutation on DM-induced SCO alternation. (A) Representative traces of SCOs in cortical neuronal cultures from WT mice (top trace) and mice carrying gain-of-function mutation (bottom trace) recorded at 7 DIV. (B) Quantification of the SCO frequency and amplitude in WT and neurons. (C) Representative SCO traces in the absence and presence of DM () in WT (upper two traces) and neurons (lower two traces). Arrowhead indicates the addition of Veh (0.1% DMSO) or DM (). The data from dashed line window were used to analyze the inhibitions. (D) Quantification of DM inhibitions on the SCO frequency and amplitude in WT and neurons. DM-induced response (% inhibition) was analyzed by normalizing to respective vehicle control (0.1% DMSO) of each genotype. The mean values of SCO frequency and amplitude of each plate were used as analysis unit. Each data points represents the from four independent sister cultures. A t-test was used to compare the statistical significance of SCO frequency and amplitude between WT and neurons as well as the SCO response of DM between two genotypes. Note: DM, deltamethrin; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; RyRs, ryanodine receptors; SCO, synchronous oscillations; Veh, vehicle; WT, wild type. *; **, WT neurons vs. neurons.