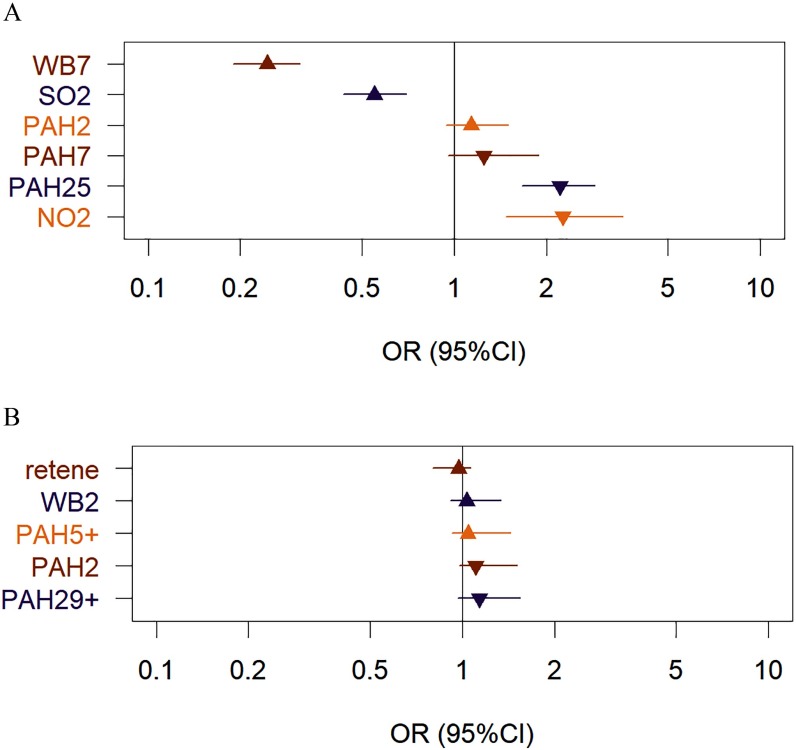
Figure 1.
Odds ratios (ORs) per 1 standard deviation increase in exposure for different exposure clusters in the full population (A) and the smoky coal subpopulation (B). Exposure clusters were polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) 25 [consisting of 25 PAHs, including benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) and 5-methylchrysene (5-MC)], WB7 [consisting of seven wood burning–associated exposures, including fine particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter ()], PAH7, PAH2, and two clusters consisting of the single exposures, nitrogen dioxide () and sulfur dioxide (), respectively (See also Table S2 for complete listing of compounds in each cluster). Note: CI, confidence interval.