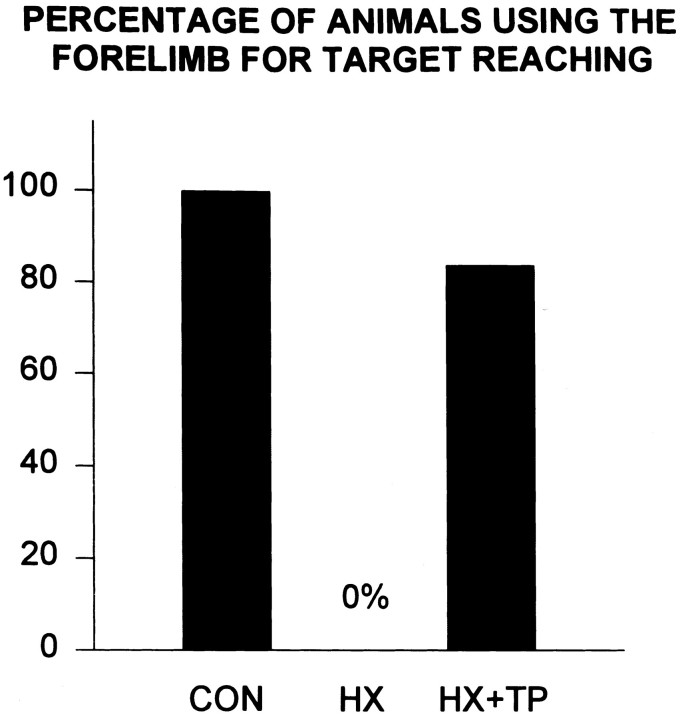
Fig. 10.
Effect of neonatal cervical spinal cord injury on target reaching. CON rats (n = 4) consistently use either forelimb to retrieve food pellets from horizontal shelves and never engage in compensatory movements. Conversely, HX rats (n = 5) consistently failed to develop both reaching and coordinated lower body responses and compensated by using tongue protraction.HX+TP rats (n = 6) use a combination of patterns, but more consistently use forelimbs to grasp a pellet.