Fig. 4.
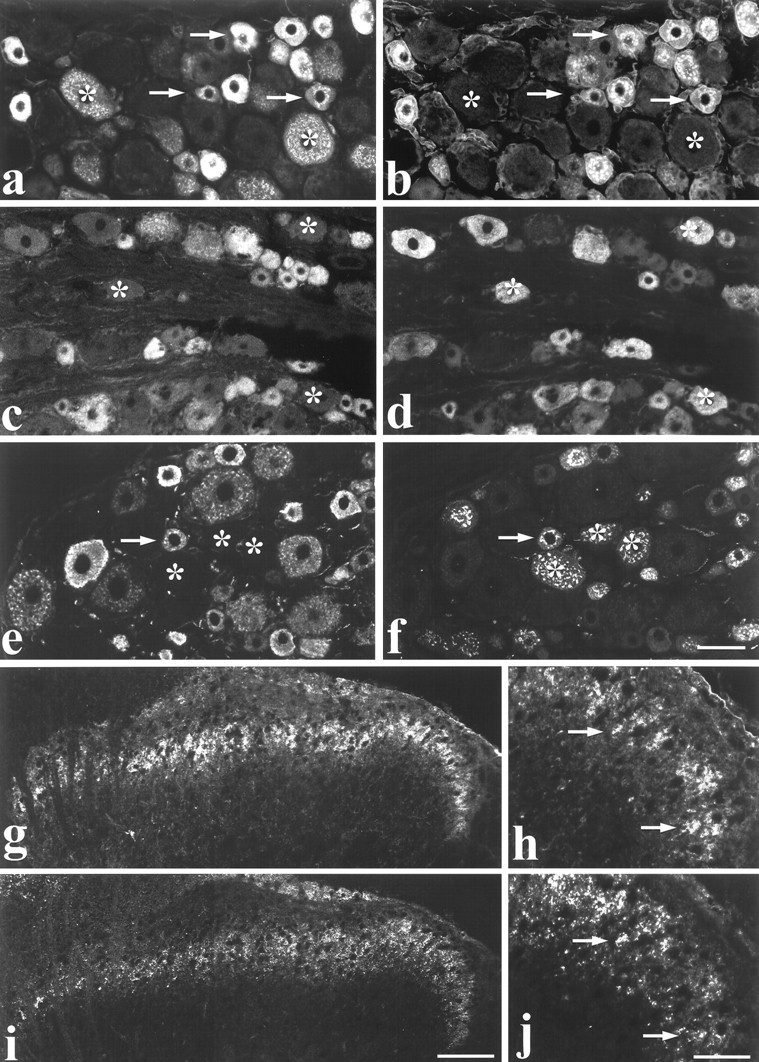
Colocalization of RET immunoreactivity with neurochemical markers in DRG cells and spinal cord.a–f, Dual labeling showing RET immunofluorescence (a, c, e) combined with IB4 labeling (b), trkA immunofluorescence (d), and CGRP immunofluorescence (f) in DRG cells. Arrowsindicate extensive colocalization of RET and IB4 in small diameter cells (a, b). Note that all IB4 cells show RET immunoreactivity. However, several RET positive cells do not bind IB4 (asterisks). RET labeling is not evident in many trkA cells (c, d). Asterisks denote trkA cells that are not co-labeled for RET. Similarly, few CGRP-expressing DRG cells are RET immunoreactive (e, f).Asterisks indicate cells that do not express RET but are labeled for CGRP. The arrow indicates a cell that is dual-labeled. g–j, Low-magnification (g, i) and high-magnification (h, j) micrographs showing RET immunofluorescence (g, h) and IB4 (i, j) double labeling in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Labeling is most intense in inner lamina II.Arrows in h and j indicate individual double-labeled axons. Scale bars (shown inf): a–f, 50 μm; (shown ini): g, i, 100 μm; (shown in j): h, j, 30 μm.
