Fig. 7.
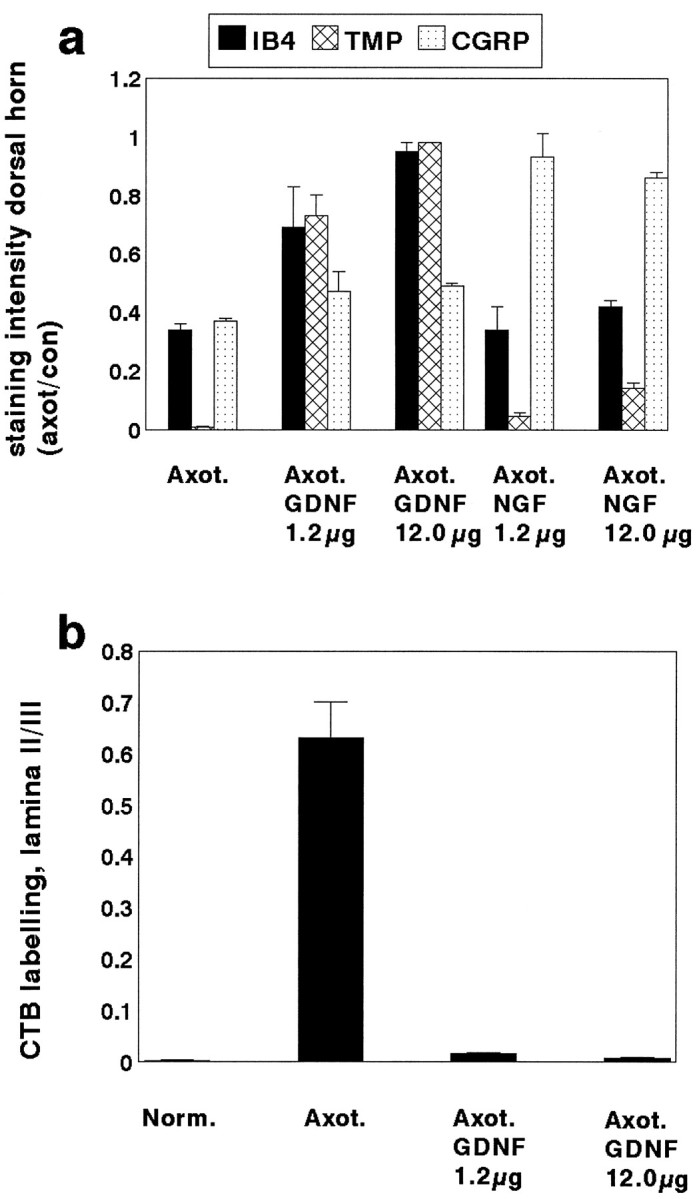
a, The ratio of the area occupied by IB4, TMP, or CGRP stained terminals within lamina II of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord on the axotomized side versus the normal side in animals that have undergone axotomy (n = 4) or axotomy in combination with an intrathecal infusion of GDNF at a dose of either 1.2 μg/d (n = 3) or 12 μg/d (n = 4) or NGF at a dose of either 1.2 μg/d (n = 3) or 12 μg/d (n = 3). GDNF at a dose of 12 μg/d almost completely prevented the axotomy-induced reduction in staining intensity of IB4 and TMP (p < 0.001; unpaired t test; comparing GDNF with no treatment after axotomy). The lower dose of GDNF (1.2 μg/d) also had a significant effect in preventing the axotomy-induced reduction in staining intensity of these markers but was less effective than the higher dose. The high dose GDNF had a small but significant effect in preventing the axotomy-induced reduction in CGRP staining (p < 0.05; unpairedt test). NGF could almost completely prevent the axotomy-induced reduction in CGRP staining (p < 0.001; unpaired t test; comparing NGF with no treatment after axotomy). NGF at 12 μg/d had a small but significant effect on the axotomy-induced reduction in IB4 and TMP expression (p < 0.05; unpairedt test). b, The ratio of the area occupied by CTB-labeled terminals in lamina II compared with lamina III of the dorsal horn in normal (n = 5), axotomized (n = 4), and axotomy + GDNF (Axot. GDNF) 1.2 μg/d (n = 3) and 12 μg/d (n = 4) animals. Note that there is a significant increase in labeling in lamina II after axotomy (p < 0.01; unpaired t test), which is almost completely prevented by treatment with GDNF at the higher dose. GDNF treatment at the low dose also had a significant effect (p < 0.01 compared with no treatment; unpaired t test) but was less effective than the higher dose.
