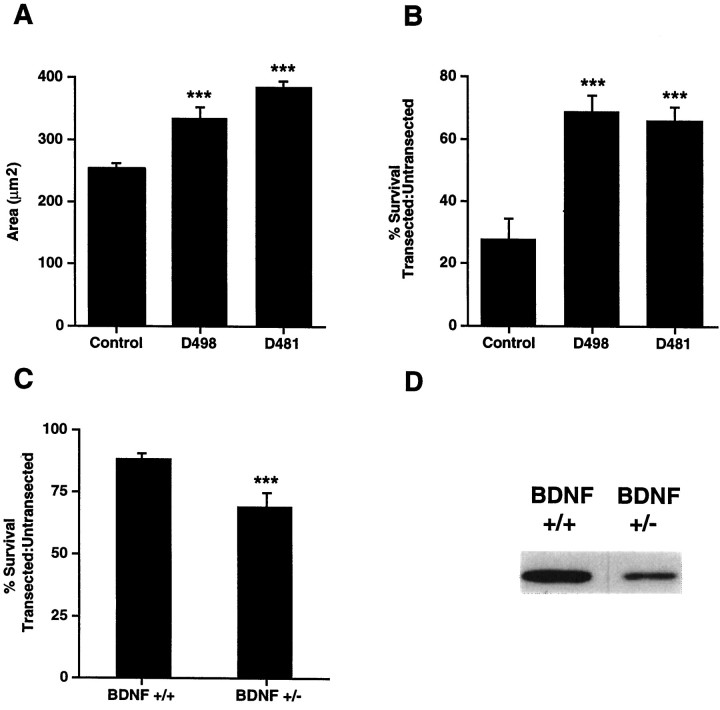
Fig. 6.
A, Facial motorneurons are hypertrophied in neonatal DBH–BDNF transgenic mice. The average cross-sectional area of P12 facial motoneurons was determined by image analysis of cresyl violet-stained coronal sections of the appropriate brainstem level of DBH–BDNF mice of lines D498 and D481 versus their control littermates. In both lines of DBH–BDNF mice, facial motoneurons were significantly hypertrophied. ***p < 0.005. B, Neonatal facial motoneurons are rescued from axotomy-induced death in DBH–BDNF transgenic animals. The facial nerves of 5-d-old control and DBH–BDNF animals were unilaterally transected, and 7 d later, serial 16 μm sections were collected throughout the entirety of the facial nuclei. The number of facial motoneurons was then determined in the contralateral, control versus ipsilateral, transected facial nuclei by image analysis quantification of the number of facial motoneurons in every fifth section. The results of this analysis are presented as a ratio of the number of neurons in the transected versus untransected nuclei. The mean number of facial motoneurons within each group is presented within the text. Note that in control littermates, only 28% of facial motoneurons remain 1 week after a facial nerve transection, whereas in lines D498 and D481, 69 and 66% of facial motoneurons remain, respectively. ***p < 0.005;n = at least three animals in each group.C, Survival of transected facial motoneurons is reduced in adult BDNF+/− mice compared with their BDNF+/+ littermates. Methods similar to those described in B were used, with the exception that unilateral facial nerve transections were performed on 3-month-old BDNF+/− versus BDNF+/+ animals. The results of this analysis are presented as a ratio of the number of neurons in the transected versus untransected nuclei. Note that in BDNF+/+ littermates, 87% of motoneurons remain 1 week after a facial nerve transection, whereas in BDNF+/− mice, only 71% of facial motoneurons remain. ***p < 0.05; n = 3 animals in each group. D, BDNF levels are decreased in the BDNF+/− brain. Western blots of equal amounts of protein from the cortex of BDNF+/− versus BDNF+/+ mice were probed with an antibody to BDNF. A similar decrease was observed in other regions of the BDNF+/− brain (data not shown).