Fig. 1.
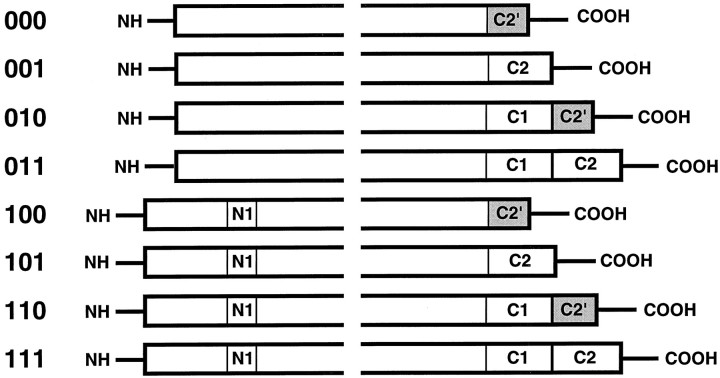
Schematic illustrating the proteins produced by alternative splicing of the NMDAR1 mRNA, after Zukin and Bennett (1995). The N- and C-terminal regions of the eight potential isoforms of NMDAR1 are illustrated. The forms are identified by a binary nomenclature (000–111) indicating the presence or absence of the various segments, as listed on the leftside. The conserved region of the proteins, containing the membrane-spanning domains responsible for channel formation, are not illustrated. The N1 insertion in the N-terminal region consists of 21 amino acids, encoded by exon 5 of the NMDAR1 gene. The C1 segment contains 37 amino acids, encoded by exon 21. Two distinct C-terminal sequences are possible, and these are determined by the use of alternative splice acceptor sites within exon 22. The C2 segment encodes 38 amino acids. If the C2 segment is omitted, the reading frame is altered, producing a unique C terminus (C2′,shaded) containing 22 amino acids.