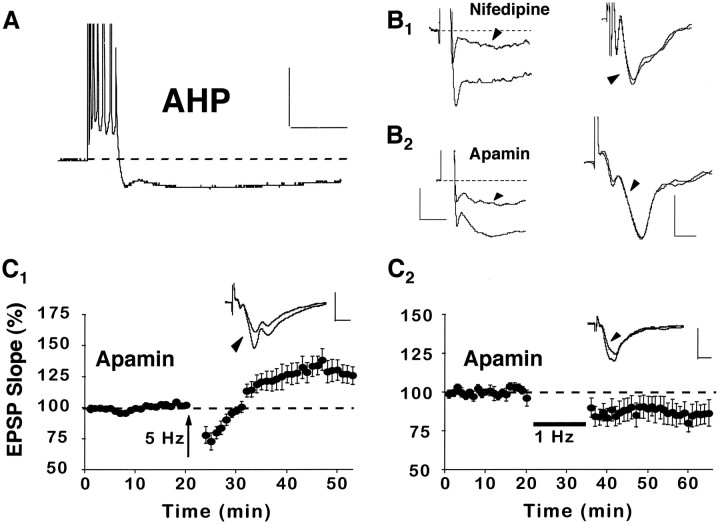
Fig. 6.
Nifedipine enhances synaptic strength via a reduction in the AHP. A, An example of an AHP recorded intracellularly from a CA1 pyramidal cell in an aged rat after a train of seven action potentials, elicited by a 100 msec pulse of depolarizing current. Calibration: 20 mV, 200 msec.B1, Illustrations of the AHP (cell held at −65 mV) after a burst of seven action potentials (left) and the field EPSP (right) before and after (arrowheads) application of nifedipine to the recording medium. B2, Illustrations of the AHP (cell held at −71 mV) after a burst of seven action potentials (left) and the field EPSP (right) before and after (arrowheads) application of the K+ channel blocker apamin (1 μm) to the recording medium. These data show that nifedipine and apamin reduce the AHP to a similar extent. However, neither drug substantially alters the EPSP slope. Waveforms inB are averages of five consecutive responses collected before and after drug wash-in. Also, in the left panels, note that action potentials were truncated to better illustrate the AHPs. Calibration: for AHPs, 2.5 mV, 200 msec; for EPSPs, 0.5 mV, 5 msec. C1, Like nifedipine, application of apamin to aged rat slices (n = 7) facilitated the induction of synaptic enhancement attributable to 5 Hz stimulation. C2, In contrast to nifedipine, apamin did not prevent the induction of LTD after 1 Hz stimulation (n = 7). Insets forC display the averaged field EPSP waveforms from 10 successive responses collected immediately before and 30 min after (arrowhead) the delivery of pattern stimulation. Calibration: 1 mV, 5 msec.