Fig. 3.
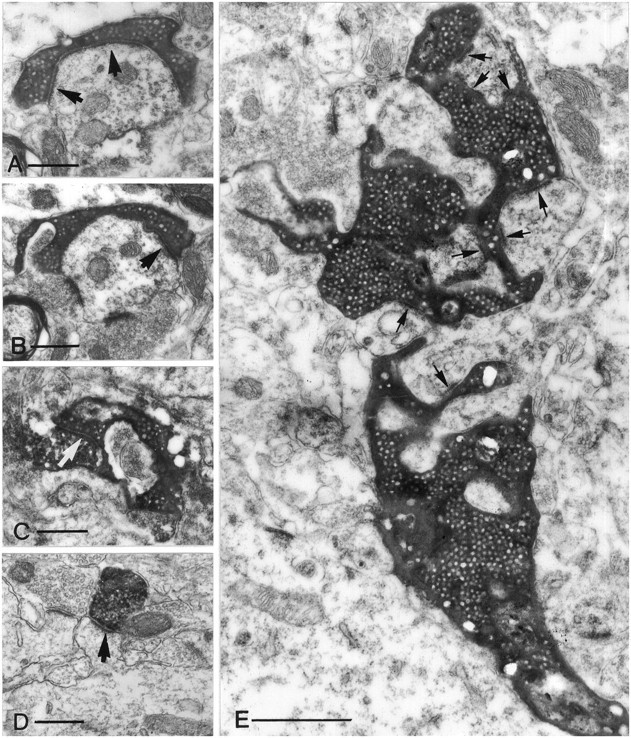
Electron micrographs of different terminal types along the mossy fibers in the CA3 region (A–C, E) and of a CA3 pyramidal cell terminal (D). All electron micrographs have the same magnification to help comparison of the relative size of the terminals. A, B, A small en passant terminal establishes a single asymmetrical synapse on a dendritic shaft with long perforated postsynaptic density (arrows). C, A filopodial extension of a mossy terminal forms a synapse (arrow) with an SPR-immunoreactive interneuron.D, The postsynaptic target of a pyramidal cell terminal is a simple spine of a CA1 pyramidal neuron. Compare this spine with the spines of GABAergic interneurons (Fig. 10). E, A large, double-headed mossy terminal forms multiple contacts (arrows) with thorny excrescences of a CA3 pyramidal cell. The individual release sites are short. Scale bars:A–D, 0.5 μm; E, 1 μm.
