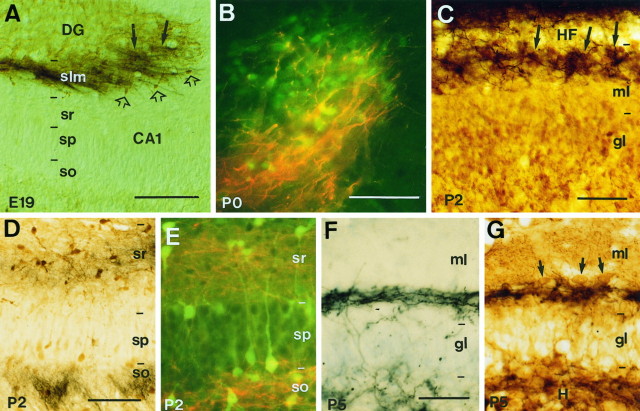
Fig. 4.
Overlapping distribution of developing hippocampal afferents and pioneer neurons in the hippocampus. A, Fascicles of entorhinal axons (black arrows) traced with biocytin overlap with Cajal-Retzius cells in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare identified by calretinin immunostaining (brown open arrows) at E19. B, High-power fluorescence photomicrograph shows entorhinal axons (red) intermingled with calretinin-positive Cajal-Retzius cells (green) at P0 in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare of the CA3 region. C, In the dentate gyrus, ingrowing entorhinal axons (black) at P2 are restricted to the outer molecular layer (close to theHF), forming patches (arrows) around the clusters of Cajal-Retzius cells (brown) in this layer. D, E, Photomicrographs show that commissural fibers traced with biocytin at P2 (D,black; E, red) arborize in the stratum oriens and in the stratum radiatum, where calbindin-positive neurons (D, brown;E, green) are located. F,G, In the dentate gyrus, commissural axons (black) are restricted to the inner molecular layer at P5, where they overlap with GABA-positive neurons (brown; arrows in G). The section in F was slightly stained with thionin. Sections were photographed under Nomarski (A, C,D, F, G) or epifluorescence (B, E) optics. Scale bars: A, 300 μm; B andE, C, F andG, 50 μm; D, 100 μm.DG, dentate gyrus; gl, granular layer;H, hilus; HF, hippocampal fissure;ml, molecular layer; slm, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; so, stratum oriens;sp, stratum pyramidale; sr, stratum radiatum.