Fig. 2.
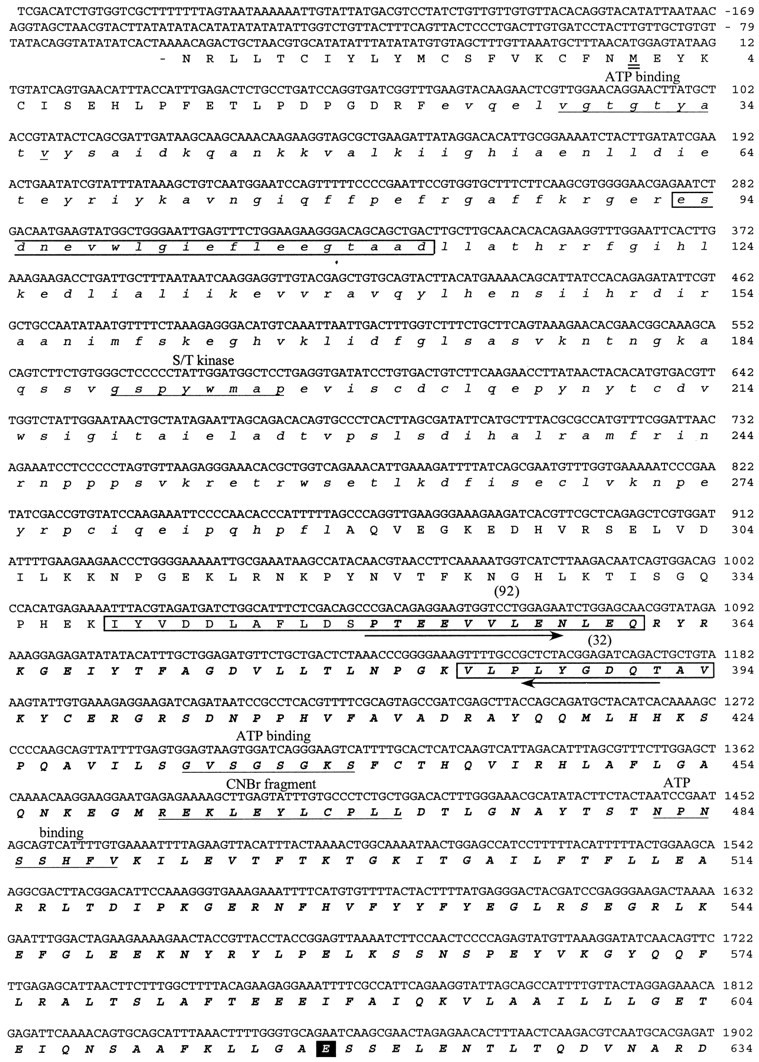

cDNA sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the 122 kDa protein. The cDNA sequence presented was determined by sequencing three different purified cDNA clones that hybridized to an initial 125 bp PCR product. The amino acid sequences against which the initial degenerate PCR primers were designed are indicted witharrows. The kinase domain of the predicted protein is shown in lowercase italics. The myosin domain is inbold uppercase italics. The amino acid sequences obtained by directly sequencing four of the tryptic peptides released from the 122 kDa protein are boxed, and the number of the peptide is indicated above the sequence. The predicted initiation methionine is underlined twice.Underlined once are the ATP binding region of the kinase domain; the S/T kinase signature sequence; sequences involved in ATP binding to the myosin domain; the N-terminal sequence of the 50 kDa phosphorylated CNBr cleavage fragment (CNBr); the region within the myosin domain that may be involved in conformational change; and the putative IQ calmodulin binding region. The TEDS site is indicated with a black square. Three serines that are consensus PKA phosphorylation sites are circled.
