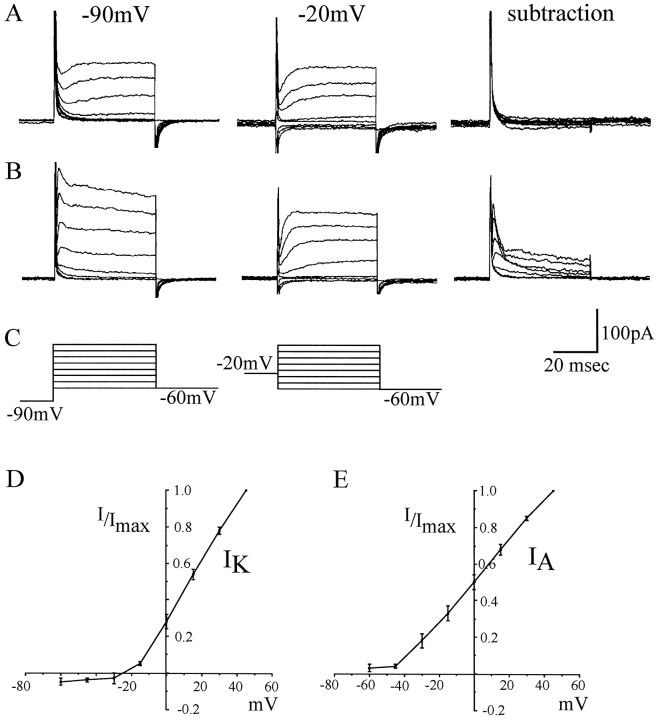
Fig. 3.
IK andIA can be separated by differences in voltage-dependent inactivation. A, Voltage-activated K currents evoked from different conditioning prepulses (−90 and −20 mV) at 16 hr AEL are essentially identical such that their subtraction from one another shows no evidence for any inactivating K-currents (which are inactivated by a prepulse to −20 mV). B, At 17 hr AEL when both IK andIA are present, a prepulse of −20 mV inactivates only IA-isolatingIK; subtraction yieldsIA. C, Recordings were obtained in K conductance saline (see Materials and Methods), and voltage steps (15 mV increments; range, −60 to +45 mV; 50 msec) were applied from conditioning prepulses of either −90 or −20 mV.D, E, Current–voltage relationships forIK and IAisolated by differential voltage-dependent inactivation. To overcome heterogeneity in current amplitude between individual neurons, currents are normalized to the maximum current (I) evoked at 45 mV in each neuron. Each point is the average of 13 (IK) or 14 (IA) determinations ± SE (average peak amplitude: IK, 64 ± 13 pA; IA, 141 ± 29 pA) from neurons 19–21 hr AEL.