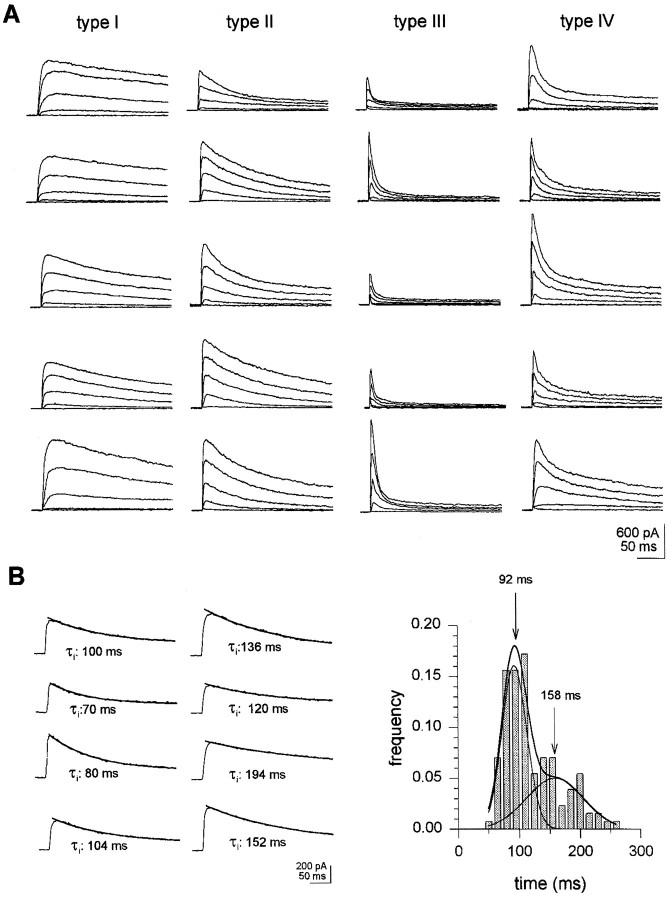
Fig. 2.
Classification of neurons in wtDrosophila larvae. Whole-cell currents were recorded as described in Materials and Methods. A, Neuron types in wt larvae. Neurons were classified based on time constants of inactivation and relative amplitude of exponential components, at V = 0 mV, as explained in Results. Records show various examples of outward current patterns in different neurons types. Outward currents were elicited by 20 mV depolarizing steps, from −60 to 20 mV, in 20 mV intervals. Holding potential was −120 mV. B. Analysis of inactivation times in neurons with outward currents inactivating along a single exponential (n = 128).Left, Single exponential outward current inactivation patterns. Currents were triggered by depolarizing excursions from a −120 mV holding to 0 mV. Lines on top of current records are best fit of single exponential function to data.Right, Distribution of inactivation times. Thesolid line is best fit to data of two Gaussian curves, with peaks at 92 and 158 msec. The relative contribution of each Gaussian component is 0.58 and 0.42, respectively;n = 128. r2 = 0.96.