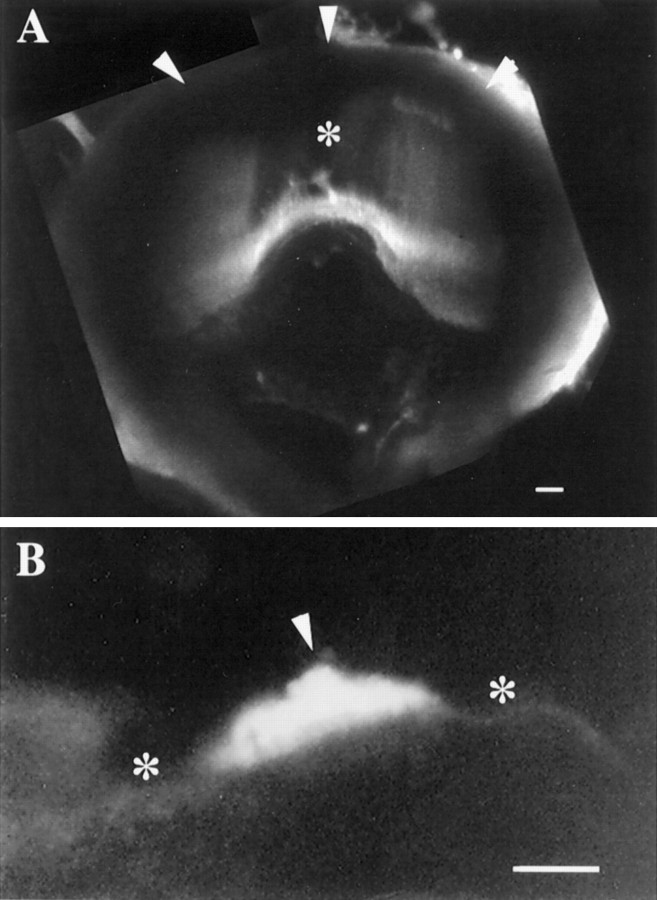
Fig. 3.
Confocal images of the cupulae of the PC and PN stained with FITC-WGA. Each image represents a superimposition of 20 (A) and 8 (B) confocal sections taken at steps of 5 μm. A, PC cupula extends from the crista surface (bottom) to the ampullary roof (top, arrowheads), forming a partition occluding endolymph flow within the posterior ampulla. Less florescence is seen over the middle of the PC (*), where the cupula is relatively thin.B, PN cupula is 35 μm at its thickest point (arrowhead) and may be seen to protrude into the endolymphatic space from the wall of the utricular sac (*). When the height of the neuroepithelium is considered (Fig. 2C), the cupula extends 60–70 μm into the lumen of the posterior utriculus. Scale bars: A, B, 50 μm.