Fig. 1.
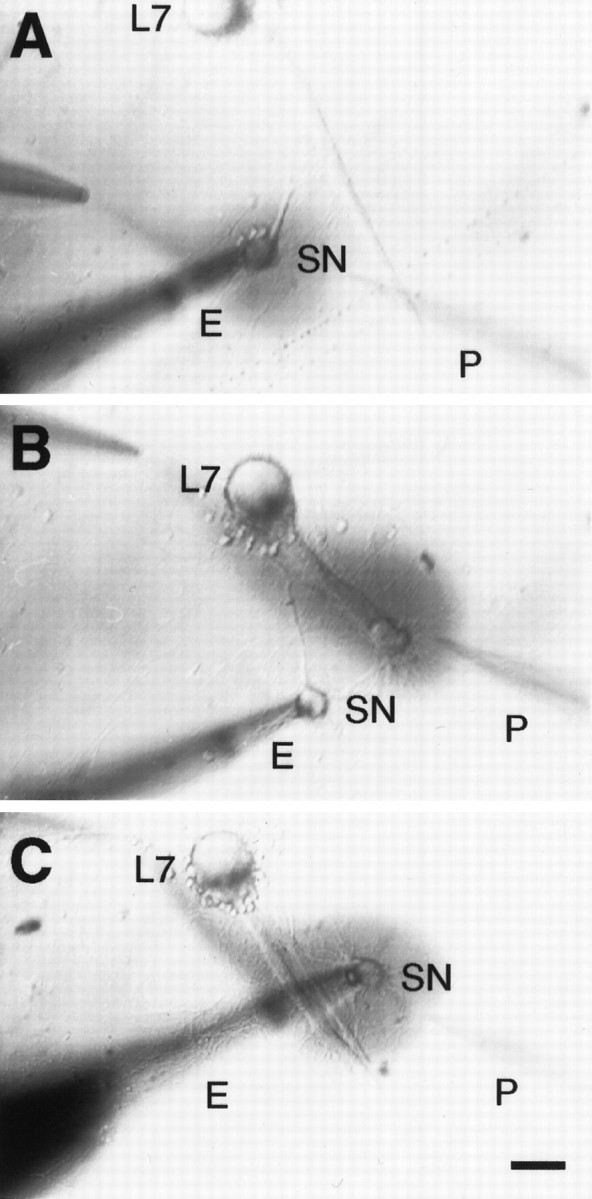
Application of 5-HT to different areas of interaction between the sensory neuron (SN) and L7. Phase-contrast micrographs of three cocultures each, with a single SN forming synaptic contacts with a single L7. The axon of L7 emerges from the cell body (top of each micrograph) and extends toward the lower right. The stump of the SN axon is always placed next to the axon of L7 so that the proximal arbor of the SN contacts the proximal axon of L7. Pressure is used to eject 5-HT plus Fast Green from the pipette (P) atright, and rapid suction is used to remove solution from the pipette at left. 5-HT solution is added to specific regions of SN–L7 interaction by positioning the pipettes at appropriate locations so that 5-HT binds to receptors on the SN cell body (A), to receptors on the terminals in the proximal portion of the SN arbor that are in contact with the axon of L7 (B), or to receptors on both the SN cell body and terminal region (C). Eindicates the extracellular electrode used to stimulate SN (single action potential or tetanus). Scale bar, 50 μm.
