Fig. 2.
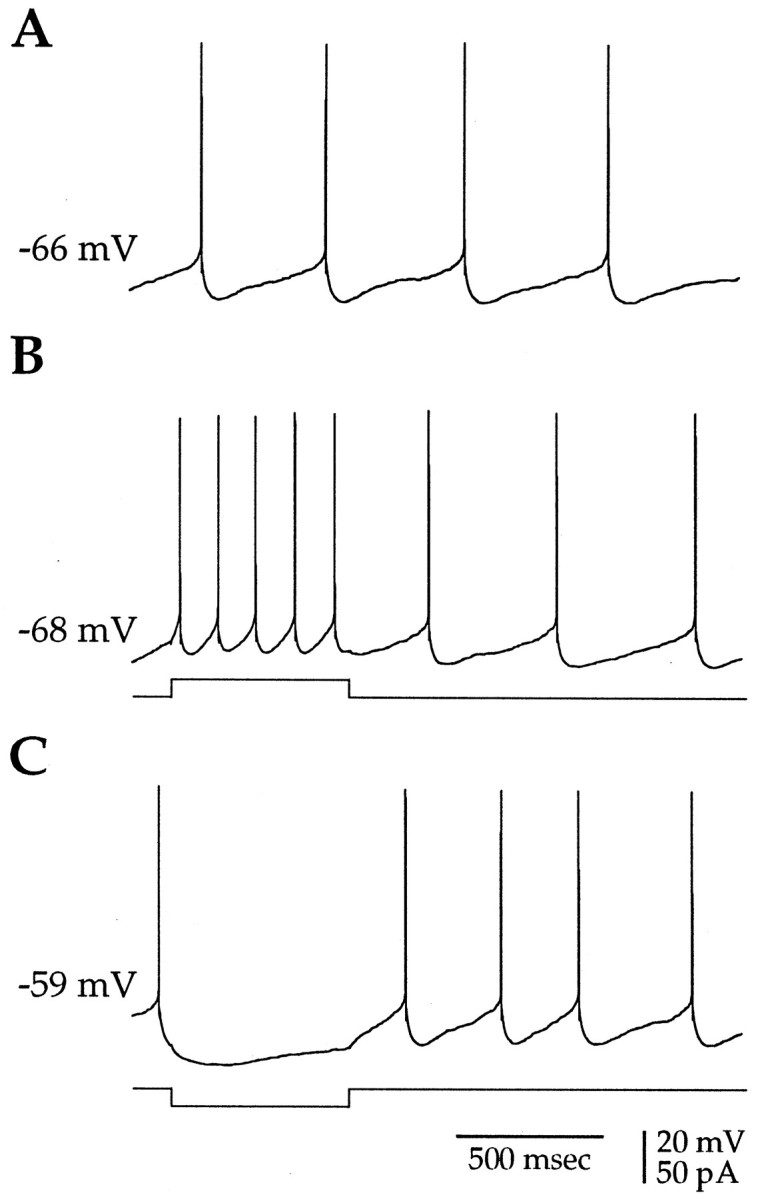
Small-amplitude current injections induce regular spiking in spontaneously active cholinergic neurons. A, The majority (>80%) of cholinergic neurons were spontaneously activein vitro. B, Depolarizing somatic current injection (20 pA, 600 msec, 0.2 Hz) was used to elicit regular spiking with a stationary interspike interval. C, Hyperpolarizing current injection (−20 pA) caused a cessation in spontaneous firing, illustrating that the spiking in cholinergic neurons was readily controlled by small-amplitude current injections. The initial membrane potential is indicated to the leftof each trace.
