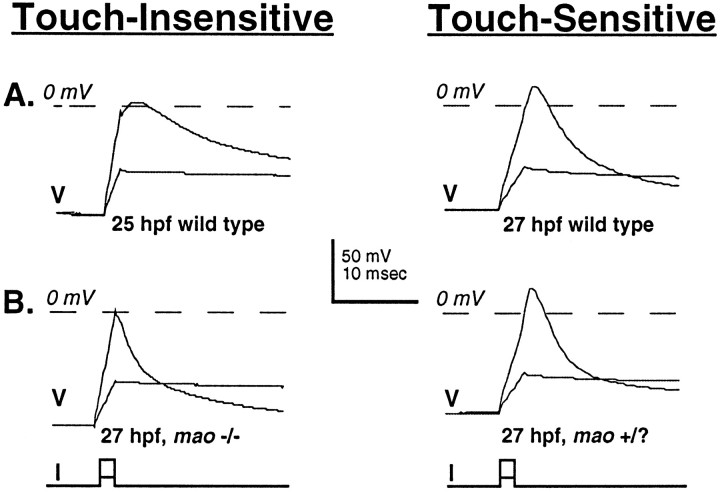
Fig. 5.
As touch sensitivity is being acquired, the amplitude of the overshoot of the action potential increases in Rohon–Beard neurons of wild-type, but not mao, homozygous embryos. A, Action potentials recorded from neurons in wild-type embryos before (25 hpf; left) and after (27 hpf; right) the acquisition of touch sensitivity. B, Action potentials recorded from neurons in unaffected sibling (right) and maohomozygous (left) 27 hpf embryos. mao−/− and +/? embryos are not distinguishable before the time that touch sensitivity normally is acquired (27 hpf). At this time the action potentials are elicited from neurons of maohomozygous embryos. However, the amplitude of the overshoot of these action potentials is small and resembles that of action potentials of neurons of wild-type embryos before the acquisition of touch sensitivity (see also Table 2).