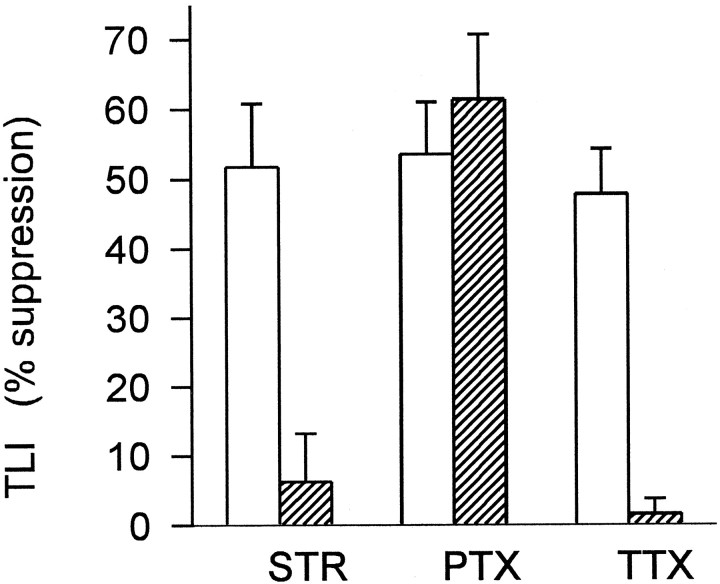
Fig. 3.
Summary of effects of strychnine, picrotoxin, and tetrodotoxin on transient lateral inhibition in ganglion cells. TLI was elicited by 1200 μm i.d. windmill stimuli, intensity 8.4 log quanta. Ordinate indicates the magnitude of TLI expressed as percentage suppression of the spot response by rotation of the windmill pattern, calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Each pair ofbars shows TLI in control Ringer’s solution (open) and in the presence of the indicated drug (hatched): 2 μm strychnine (STR) (n = 6 cells), 150 μm picrotoxin (PTX) (n = 3 cells), and 500 nm tetrodotoxin (TTX) (n = 6 cells). In three of the cells both strychnine and TTX were tested. Error bars indicate 1 SEM. Strychnine and TTX each caused a significant decrease in TLI (p = 0.004 and 0.003, respectively; paired Student’s t test), but picrotoxin did not (p = 0.45). For comparison, the data shown above include only those cells in which the spot and windmill intensities were 8.4 log quanta, but similar results were obtained in other cells from both tiger salamander and mud puppy using windmill stimuli of other intensities.