Fig. 7.
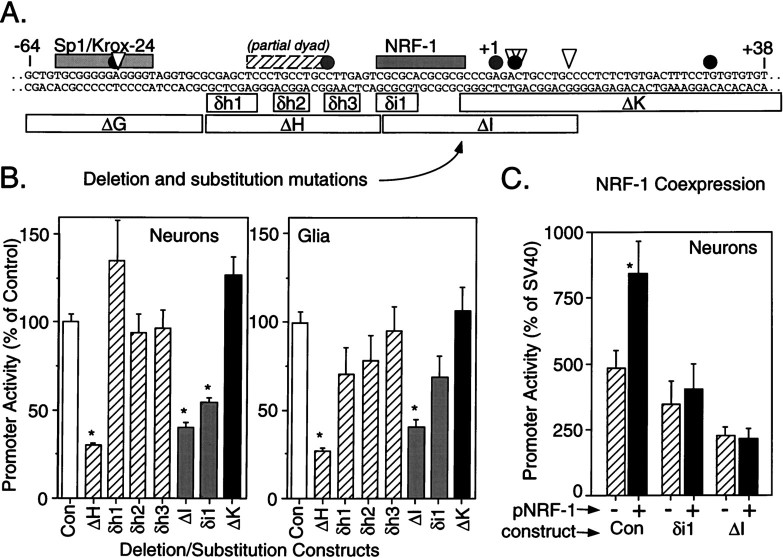
Contribution of the NRF-1 element to GluR2 promoter activity. A, Schematic of the positive regulatory domain, −64 to +38 bp, of the GluR2 promoter region is shown with regulatory cis elements as shaded barsabove the sequence;gray and solid circles andtriangles signify some of the transcription initiation sites described in the Figure 1A legend. Internal deletion and substitution mutations introduced into the R2(−302/+320)luc construct are shown by open bars below the sequence and identified. Deletion mutants are signified by “Δ,” and base-for-base substitution mutations are signified by “δ.” Deletion constructs are the same as those in Figure 5. B, Multiple plasmid DNA preparations for each construct were transfected into cultured cortical neurons or cortical glia, and luciferase activity was measured 1 d later. Promoter activity of the mutated constructs was compared with that of the R2(−302/+320)luc control construct (Con). The δh1, δh2, and δh3 substitution mutations had no effect on GluR2 promoter activity in neurons and glia and did not replicate the effect of the larger ΔH deletion construct, indicating that the effect of the ΔH deletion is not dependent on nucleotide sequence (i.e., the partial dyad). In contrast, both the ΔI and δi1 mutations resulted in a reduction in promoter activity in neurons and glia, whereas the ΔK and δh3 constructs that modify the sequence immediately adjacent to the NRF-1 element were without effect. Together these results identify the consensus NRF-1 as a positive regulator of GluR2 promoter activity. Results shown are the mean ± SEM for 8–12 plasmid transfections into four to five cultures. *p < 0.05 from the control group by ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett’s tests. C, One microgram of a plasmid expressing the NRF-1 transcription factor (black bars) or an empty pcDNA3 vector (cross-hatched bars) was cotransfected with 0.5 μg of R2(−302/+320)luc (Con) or the δi1 or the ΔI mutation constructs into neurons. Data were normalized to the activity of a parallel SV40-luctransfection in each experiment. The NRF-1 cotransfection increased promoter activity in the control construct but not in those constructs with a compromised NRF-1 cis element. Results are the mean ± SEM in five neuronal cultures. *p < 0.05 from the pcDNA3- (no NRF-1) transfected group, Student’st test.