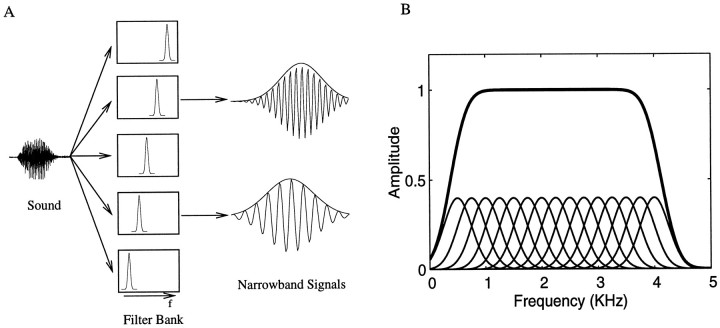
Fig. 1.
A, Schematic showing the decomposition of a complex sound into a set of narrowband signals, each described by an amplitude envelope and a frequency-modulated carrier. The complex sound is the input to a filter bank composed of a set of adjoining, and in this case overlapping, filters that cover the frequency range of interest. The narrowband output signals of two of the filters in the bank is shown. The envelope that was obtained with the analytical signal is drawn. The carrier frequency is centered at the frequency corresponding to the peak of the filter and has slow frequency modulations that are not easily discernible in this figure.B, Overall filter transform (thick line) obtained from a set of overlapping Gaussian filters (thin lines), the center frequencies of which are separated by one bandwidth (1 SD). The overall filter transform is almost perfectly flat for a large frequency range. In this example, we used 15 Gaussian filters with a bandwidth of 500 Hz and center frequencies between 500 and 4000 Hz.