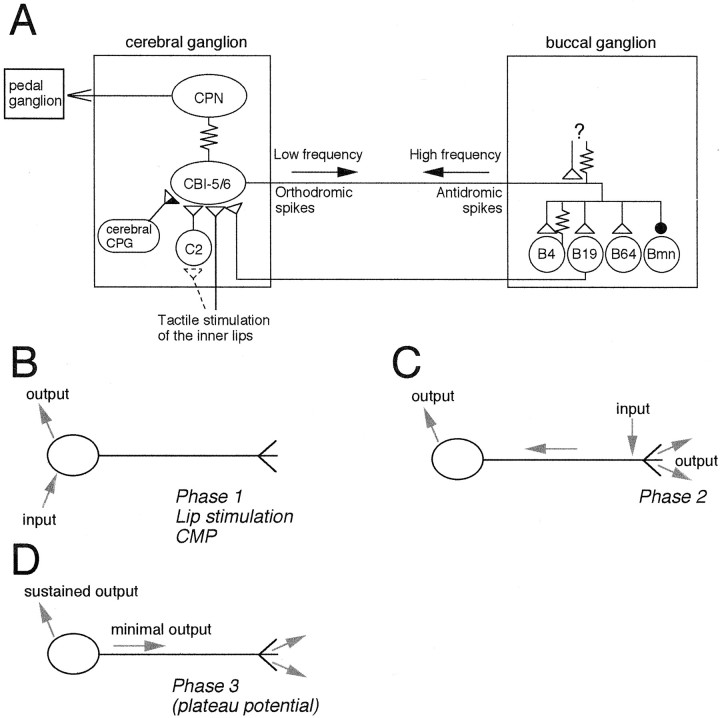
Fig. 12.
Summary of the cerebral and buccal connections of CBI-5/6. A, In the cerebral ganglion the soma of CBI-5/6 is electrically coupled to CPN1 and receives input from the cerebral CPG and from mechanical stimulation of the lips. This is likely to be in part mediated via excitation of mechanoafferent C2. The soma of CBI-5/6 is also excited by BCIs such as B19. In the buccal ganglion the distal processes of CBI-5/6 make chemical and electrical connections onto a variety of motor and premotor neurons of the feeding circuitry. The buccal processes are also excited either chemically or electrically from an unidentified source (?) to drive the antidromic spikes of phase 2 during BMPs. B–D, Different form of information flow through CBI-5/6 B, CBI-5/6 can process information through its soma yet have minimal influence on buccal events. This occurs whenever the soma is excited by cerebral inputs: during phase 1 of BMPs, in response to lip stimulation, and during the CMP. C, Input to the buccal processes generates high-frequency antidromic spiking that results in strong output in both buccal and cerebral ganglia (see Discussion for details). This occurs during phase 2 of BMPs. D, Once in the plateau potential (during phase 3 or in response to other sources of excitation to the soma), output from CBI-5/6 locally will be sustained without any inputs. Output in the buccal ganglion will again be low because of the low orthodromic firing rate.