Fig. 6.
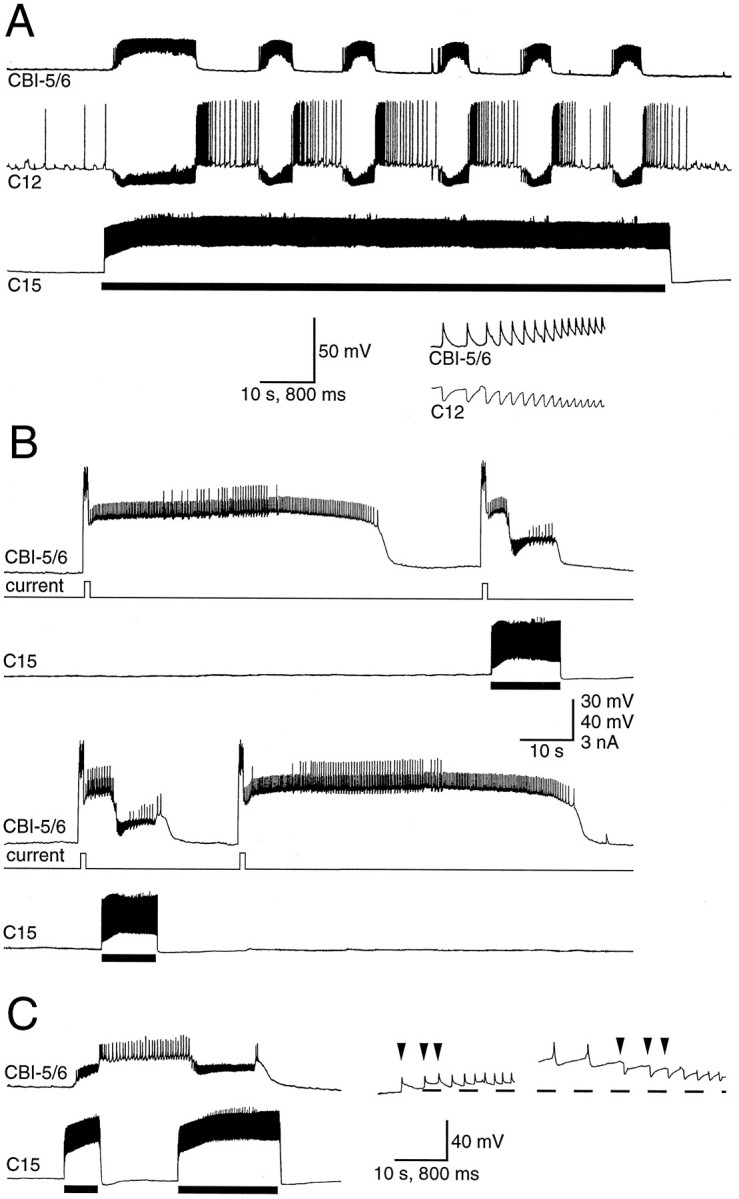
Input to CBI-5/6 during the CMP. A, The CMP was driven by injecting tonic depolarizing current into C15 (solid bar). The input to CBI-5/6 consisted of barrages of fast PSPs that were one-for-one with the fast IPSPs in lip motoneuron C12 (time-expanded bottom trace).B, A brief depolarizing current pulse in CBI-5/6 gave rise to a plateau potential that spontaneously terminated after 54 sec, and the next two plateau potentials terminated early (after 13–14 sec), after PSPs received during one cycle of the CMP driven by depolarization of C15 (shown by bar). A forth plateau terminated spontaneously after 62 sec. Records are consecutive.C, An example in which the plateau potential in CBI-5/6 could be both terminated and terminated by E/IPSPs during the CMP. A first cycle of the CMP produced by current in C15 (first bar) resulted in depolarizing E/IPSPs in CBI-5/6 that drove it into a plateau. A second cycle (second bar) terminated the plateau. The faster time base records to the rightshow that the E/IPSPs (the first three PSPs of each CMP cycle are indicated by the arrowheads) were depolarizing from rest (−54 mV in this case) but hyperpolarizing from the plateau potential (−29 mV).
