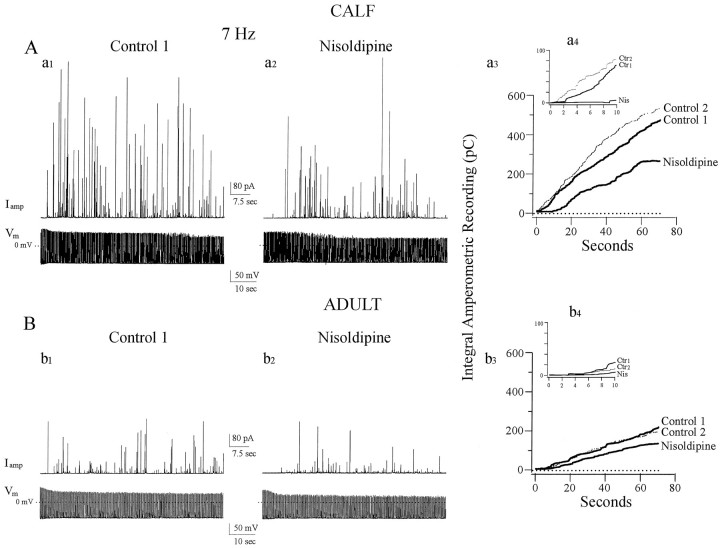
Fig. 3.
Distinct role of facilitation Ca channels in catecholamine secretion from calf AC cells. A, Calf AC cells were stimulated with trains of APs in current-clamp mode together with amperometric detection of catecholamine secretion. Amperometric spikes (Iamp) were generated in response to trains of single APs (Vm) evoked by short depolarizing current pulses at a frequency of 7 Hz (a1). Sequential trains of 490 APs at 7 Hz resulted in successive secretory episodes monitored as barrages of amperometric spikes; a 6 min rest period separated each train. As quantitated by the cumulative integral of the amperometric current (a3), the second round (Control 2) was always slightly increased relative to the first (Control 1), indicating that secretion shows no sign of exhaustion under these conditions (average increase in the second round was 12.8 ± 0.9%; n = 44). To determine whether facilitation Ca channels contribute to catecholamine secretion in calf AC cells, nisoldipine was added between trains. Secretion was substantially reduced under these conditions (a2, a3, 44% inhibition compared with secretion in the first round). Inset(a4) shows expanded time base for the first 10 sec of AP-stimulated secretion. When facilitation Ca channels are recruited (Ctr1 and Ctr2), secretion starts within the first second of stimulation, whereas after nisoldipine (Nis) secretion only starts after a lag of ∼9 sec. B, Adult AC cells treated under conditions identical to those shown in A. Instead of enhancement, a slight depression in cumulative secretion was seen in the second round of stimulation (b3, Control 1, Control 2). When nisoldipine was applied before the second round of stimulation, the signal was further depressed (b2,b3, 37% inhibition) indicating that conventional L-type Ca channels contribute to secretion in these cells.Inset (b4) shows that all three types of Ca channels found in adult AC cells promote secretion, but with an average lag of 6 sec; after nisoldipine the lag is ∼9 sec.