Fig. 3.
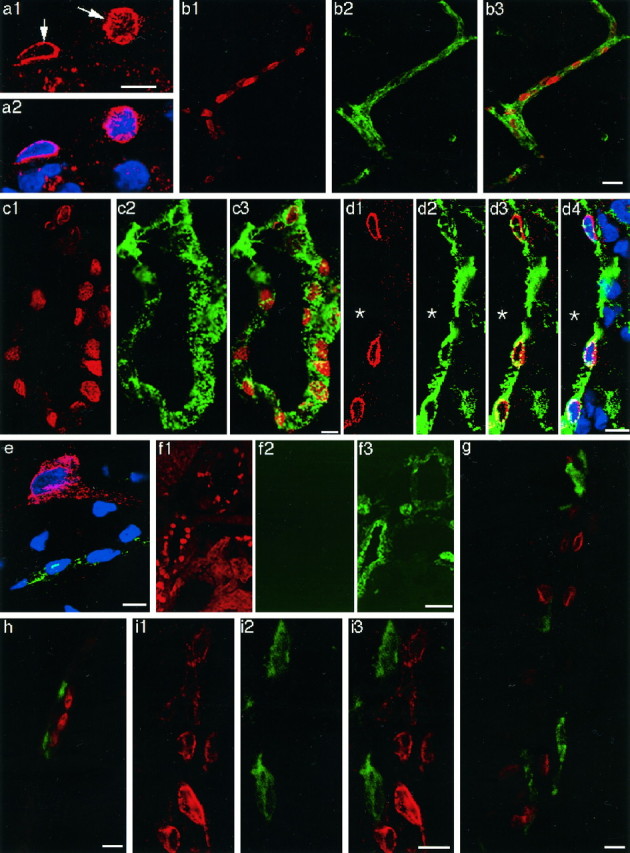
Laser confocal immunofluorescent views of COX-2-positive cells in the brains of LPS-treated rats.a1, COX-2-ir structure (arrows) in the cells of a blood vessel; a2, the COX-2 staining ina1 was overlaid with TOTO-3 nuclear staining (blue). Note that the COX-2-like immunoreactivity was restricted to the surface of the nucleus. COX-2-ir cells in parenchymal (b1) and subarachnoidal (c1, d1) blood vessels. The same blood vessels in b1, c1, andd1 were stained with anti-von Willebrand factor (b2, c2, and d2, respectively). The COX-2 immunostaining (red) was overlaid with von Willebrand factor immunostaining (green) (b3, c3, and d3). d4, The double immunostaining in d3 overlaid with TOTO-3 nuclear staining (blue); e, triple staining of COX-2 (red), von Willebrand factor (green), and nucleus (blue). Note that a neuron was positive for COX-2 but negative for von Willebrand factor; a capillary was positive for von Willebrand factor. COX-2-like immunoreactivity in the neuron was diffusely distributed in the soma and a process. f, A brain section was first stained for COX-2 (f1) and then incubated with FITC-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG without a previous incubation with anti-von Willebrand factor (f2). Note that fluorescent signal of FITC was very low compared with that in the adjacent section, which had been first stained for COX-2 and then stained for anti-von Willebrand factor as described in Materials and Methods (f3), indicating that cross-binding of FITC-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG to anti-COX-2 was negligible. Double immunostaining of COX-2-ir cells (red) and ED2-positive macrophages (green) in parenchymal (g) and subarachnoidal (h) blood vessels. COX-2-ir cells (i1) and OX-42-positive cells (i2) were located close to each other but were distinct from one another (i3). Scale bars: 10 μm;b, 20 μm; f, 50 μm.
