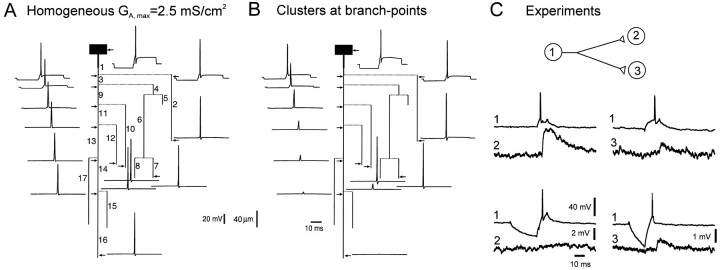
Fig. 3.
Propagation of the AP after a hyperpolarizing prepulse. A, Simulations for homogeneous distribution of A-channels (GA,max = 2.5 mS/cm2). AP was elicited after a 20 msec hyperpolarizing prepulse of 9.5 mV. No conduction failure was induced.B, Clustered distribution as in Figure2D. The same hyperpolarization induced propagation failures along the principal axon (branch 16) and collateral 12 but not in adjacent collaterals (2, 7, and 10).C, Selective conduction block in CA3 cells of hippocampal slice cultures. Pairs of two monosynaptically CA3 pyramidal cells were recorded intracellularly. Presynaptic AP induced in the cell (1) at the RMP evoked an EPSP in cell (2). When cell (1) was phasically hyperpolarized, no EPSP was elicited in the cell (2). The electrode was then removed from the cell (2) and inserted in the cell (3). Even in the presence of phasic hyperpolarization, the presynaptic AP always evoked an EPSP. AP thus failed in the axonal collateral of cell (1) to cell (2), but not in the branch to cell (3).