Fig. 1.
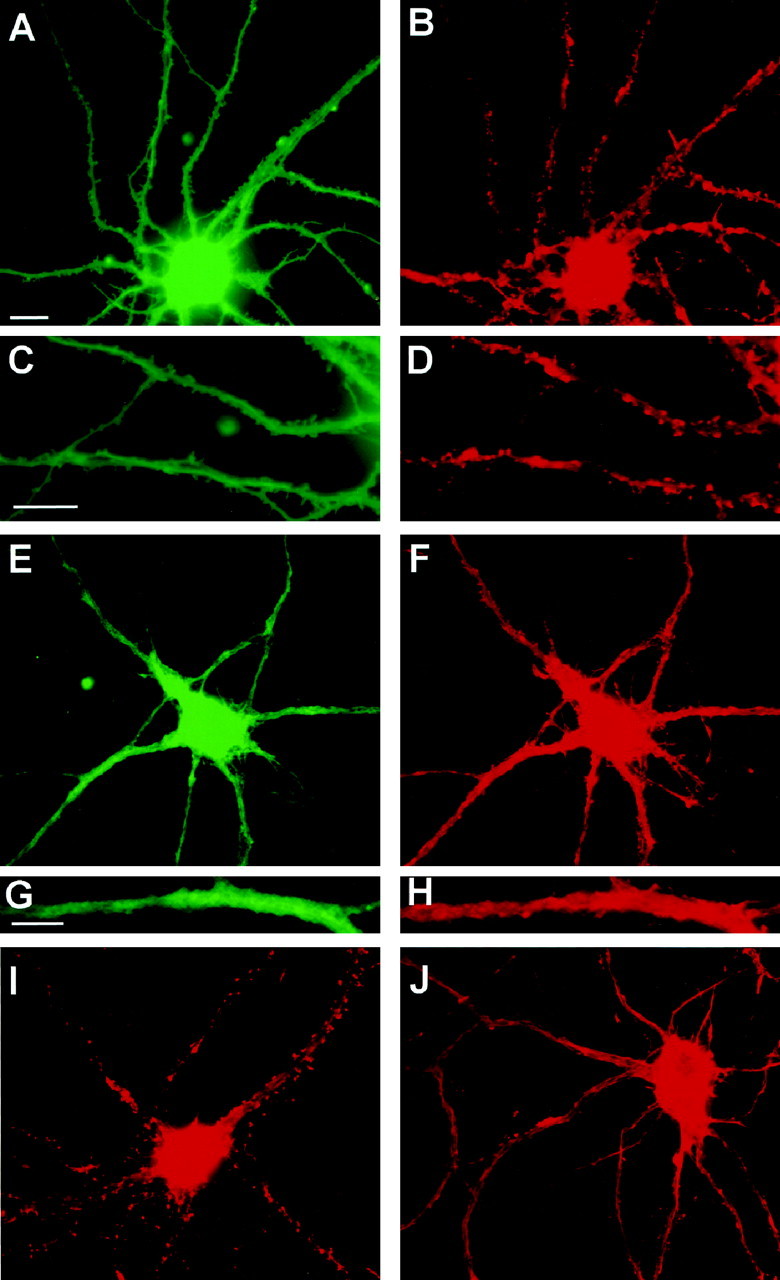
Parallel reduction in spines and F-actin punctae after glutamate receptor stimulation. A–H, Cultures were incubated in the absence (A–D) or presence (E–H) of 50 μm NMDA for 5 min before double-labeling with DiI to stain plasma membrane (A, C, E, G) or with Oregon Green phalloidin to stain F-actin (B, D, F, H). F-actin punctae colocalize with spine-like protrusions of the plasma membrane in control neurons. DiI labeling in NMDA-treated neurons was typically less uniform than that in control neurons. C, D,G, and H are enlargements of dendritic regions in A, B, E, andF, respectively. Note the close correspondence of spine-like profiles with F-actin punctae in the control neuron but not in the NMDA-treated neuron. I, J, Cultures were incubated for 5 min in the absence (I) or presence (J) of 50 μm NMDA before fixation and staining with rhodamine–phalloidin alone. The contrast in J was increased to illustrate clearly the relatively nonpunctate nature of F-actin staining after NMDA stimulation; however, pixel values over the cell body and dendrite shaft were similar in the original digital images for Iand J, which were obtained using identical image collection times and neutral density filters. Scale bars:A, B, E, F,I, J, 10 μm; C,D, 10 μm; G, H, 5 μm.
