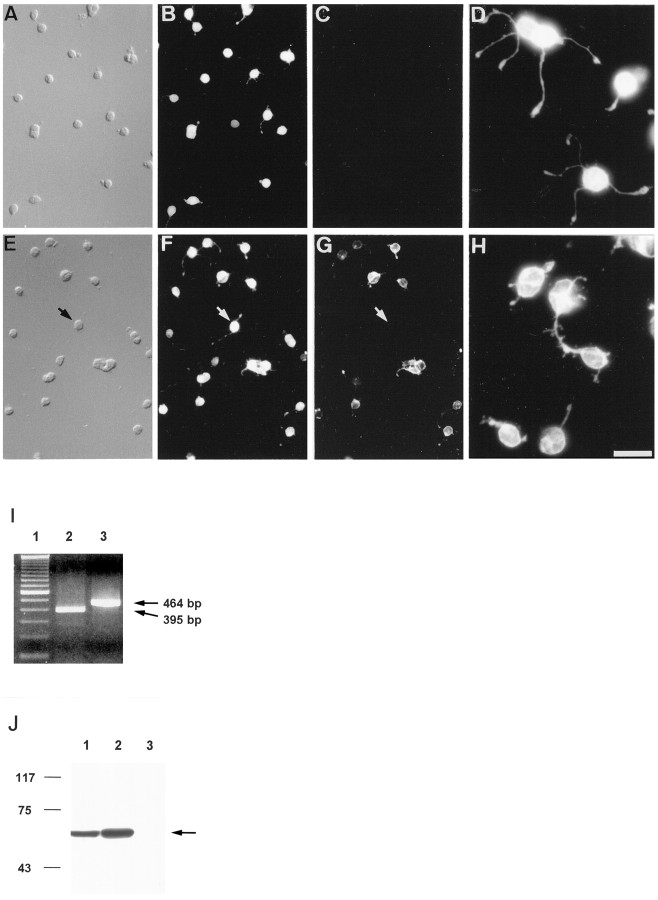
Fig. 3.
Immunocytochemical and molecular characterization of PR cultures after 24 hr in vitro.A–C and E–G show double-immunolabeling of PR cultures with antibodies specific for recoverin (B), vimentin (C), arrestin (F), and rhodopsin (G). All the cells were positive for recoverin and arrestin, indicating that they were PRs. Rhodopsin-immunopositive PRs represented only 30% of total PRs at this time (the arrow in E–Gindicates an arrestin-immunopositive, opsin-immunonegative PR). Vimentin-immunopositive cells were absent. D andH represent higher magnifications of recoverin- and rhodopsin-immunopositive PRs, showing small neurites. Scale bars:A–C, E–G, 25 μm; D, H, 10 μm.I, Expression analysis of rhodopsin (lane 2) and arrestin (lane 3) mRNA in PR cultures was examined by RT-PCR. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder.J, A comparative analysis of vimentin expression in OR (lane 1), IR (lane 2), and PR cultures (lane 3) was performed by Western blot. Although a single band of the expected molecular weight for vimentin was observed in OR and IR preparations (arrow), no signal could be detected in PR cultures.