Fig. 9.
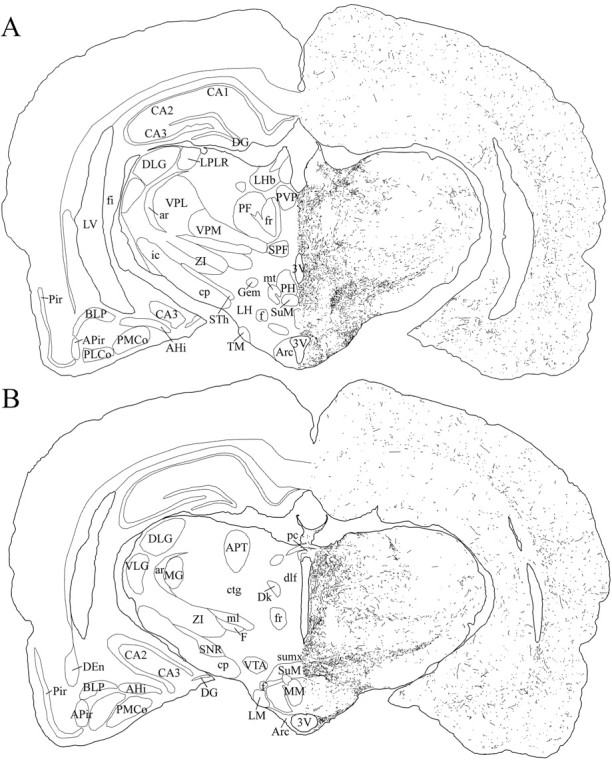
Schematic drawings of 20 μm rostrocaudal coronal sections illustrating the distribution and relative density of hcrt fibers in the caudal part of the hypothalamus after immunohistochemistry for hcrt using antibody #2050. 3V, 3rd ventricle; AHi, amygdalohippocampal area;APir, amygdalopiriform transition area;APT, anterior pretectal nucleus; ar, acoustic stria; Arc, arcuate nucleus;BLP, basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part;CA1–CA3, fields CA1–CA3 of Ammon’s horn;cp, cerebral peduncle; ctg, central tegmental tract; DEn, dorsal endopiriform nucleus;DG, dentate gyrus; Dk, nucleus Darkschewitsch; dlf, dorsal longitudinal fasciculus; DLG, dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus;f, fornix; F, nucleus of the fields of Forel; fi, fimbria of the hippocampus;fr, fasciculus retroflexus; Gem, gemini hypothalamic nucleus; ic, internal capsule;LH, lateral hypothalamic area; LHb, lateral habenular nucleus; LM, lateral mammillary nucleus; LPLR, lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterorostral part; LV, lateral ventricle;MG, medial geniculate nucleus; ml, medial lemniscus; MM, medial mammillary nucleus, medial part;mt, mammillothalamic tract; pc, posterior commissure; PF, parafascicular thalamic nucleus;PH, posterior hypothalamic area; Pir, piriform cortex; PLCo, posterolateral cortical amygdaloid nucleus; PMCo, posteromedial cortical amygdaloid nucleus; PVP, paraventricular thalamic nucleus, posterior part; SNR, substantia nigra, reticular part; SPF, subparafascicular thalamic nucleus;STh, subthalamic nucleus; SuM, supramammillary nucleus; sumx, supramammillary decussation; TM, tuberomammillary nucleus;VLG, ventral lateral geniculate nucleus;VPL, ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus;VPM, ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus;VTA, ventral tegmental area; ZI, zona incerta.
