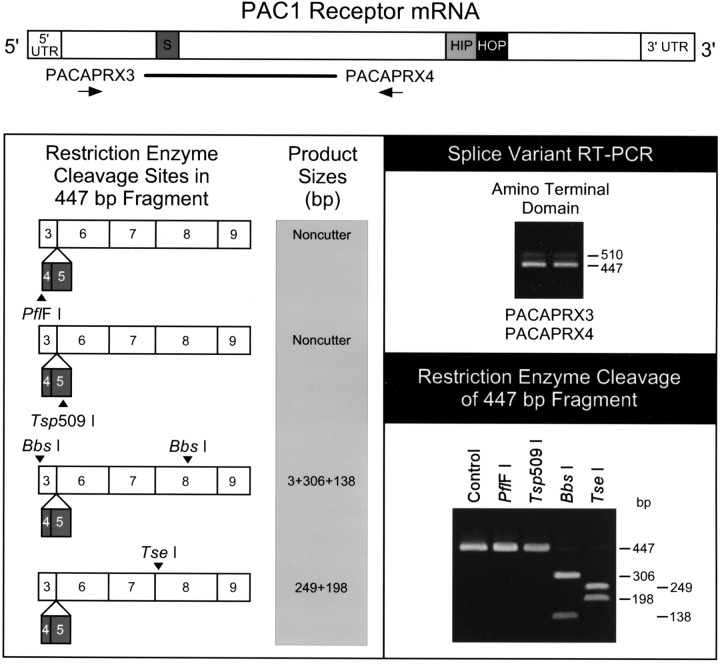
Fig. 4.
Cardiac ganglia express the very shortPAC1 receptor isoform. Complementary DNA templates were reverse-transcribed from guinea pig atrial cardiac ganglia tissue total RNA, and a segment spanning the extracellular amino terminal splice sites of the PAC1 receptor mRNA was amplified using primers PACAPRX3 and PACAPRX4 (schematic diagram, top). The prominent amplified product was 447 base pairs in size corresponding to thevery short isoform of the PAC1 receptor, which does not contain exon 4 (21 nucleotides) and exon 5 (42 nucleotides) (right panel, top). The 510 base pair product corresponding to the short variant containing the two alternatively spliced exons was lower in abundance. The 447 base pair amplified product was recovered from 1.6% agarose gels for diagnostic restriction analyses with a panel of enzymes (left panel). Enzymes PflF I and Tsp509 I, with sites unique to the short receptor variant, failed to cleave the 447 base pair product. Endonuclease digestion of the product with Bbs I or Tse I yielded the anticipated fragments for the region of the PAC1 receptor cDNA without the 63 base pair insert (left panel; right panel, bottom). Control is the undigested amplified 447 base pair product. The mRNA schematic diagram is based on the rat PAC1 receptor sequence [Spengler et al. (1993); GenBank Z23272]. Dark gray, Short region containing exons 4 and 5; light gray, HIP cassette;black, HOP cassette; thick line, region amplified using PACAPRX3 and PACAPRX4. Numbers in the schematic diagram of the restriction enzyme cleavage sites in the 447 bp fragment refer to the regions of the exons represented in the product (Chatterjee et al., 1997).