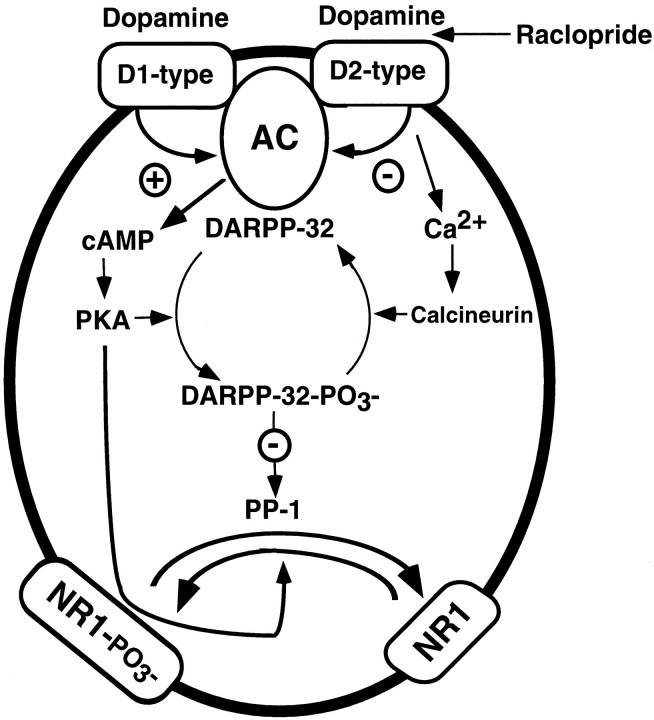
Fig. 7.
Proposed mechanism for regulation by dopamine of the state of phosphorylation of NR1. In this model, dopamine, by activation of D1-type DA receptors, increases adenylyl cyclase activity, leading to formation of cAMP and activation of PKA. Activated PKA phosphorylates both NR1 and DARPP-32. Phosphorylated DARPP-32 inhibits dephosphorylation of NR1 by PP-1. The activation of D2-type DA receptors, which is blocked by raclopride, (1) inhibits cAMP formation, leading to a decreased phosphorylation both of NR1 and of DARPP-32, and (2) increases calcium-dependent activation of calcineurin (Nishi et al., 1997), leading to increased dephosphorylation of DARPP-32.D1-type, D1-type dopamine receptor;D2-type, D2-type dopamine receptor; AC, adenylyl cyclase; PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase;DARPP-32, dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein ofMr 32 kDa; PP-1, protein phosphatase-1; NR1, NMDA receptor subunit NR1.