Fig. 2.
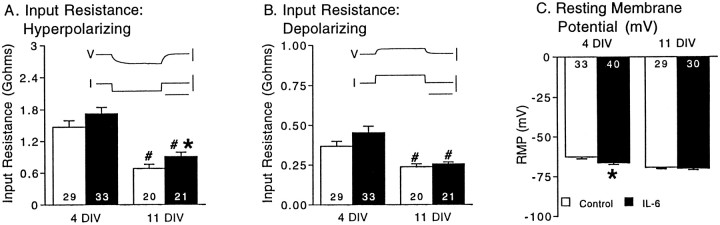
IL-6 has only minor effects on passive membrane properties and resting membrane potential in cerebellar granule neurons. A, B, Neuronal input resistance determined in current-clamp studies from the slope of current–voltage (I–V) curves at two developmental stages, 4 and 11 DIV. The I–V curves were generated from resting membrane potential (approximately −70 mV) by applying a series of hyperpolarizing or depolarizing current pulses.Insets show representative voltage recordings elicited by hyperpolarizing (A) or depolarizing (B) current pulses in control neurons.V, Voltage; calibration, 50 mV. I, current; calibration, 100 pA. Time calibration, 100 msec.C, Mean ± SEM values for resting membrane potential (RMP) at the same developmental stages. Significant (p < 0.05) effects of IL-6 are indicated by asterisks. Significant (p < 0.05) age-dependent differences within the same treatment group are indicated by number signs.Numbers in the bars indicate the number of cells studied.