Fig. 2.
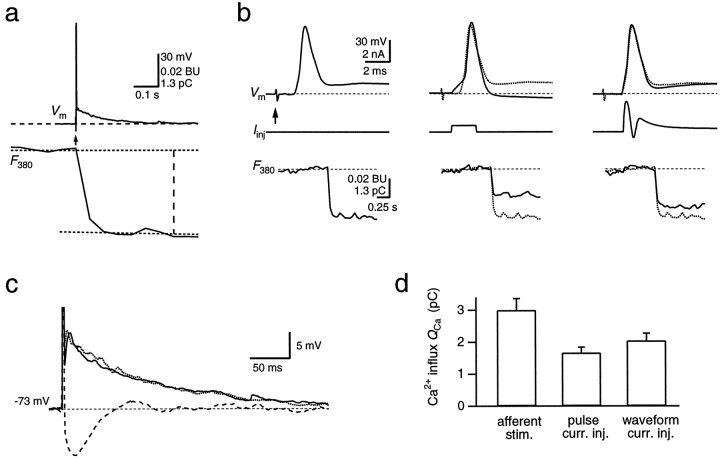
Ca2+ influx during a suprathreshold EPSP. a, A single postsynaptic AP (top, Vm) in an MNTB principal neuron evoked by afferent stimulation (arrow) displays a fast spike and a slowly decaying afterpotential. The simultaneously recorded fluorescence change (F380) on the same time scale was analyzed ∼400 msec after stimulation, as indicated by thevertical dashed line. It was evaluated as the difference between the fluorescence baseline and a straight line fit to the first 20 sample points after the fluorescence decrease.F380 is an average of eight sweeps. The decrement is expressed in bead units, as well as in picocoulombs, after conversion to Ca2+ charge. b, Single APs were evoked by either afferent stimulation (left,arrow), a rectangular current injection pulse (middle; 300 pA for 2 msec), or a waveform current injection (right). Membrane potential (Vm), the injected current (Iinj), and the simultaneously measured fluorescence intensity (F380) are shown. Note the different time scale of the fluorescence record. For comparison, the voltage trace and F380measured with the afferent stimulation protocol (dotted traces, middle and right) are overlaid with the traces measured by the current injection protocols. The different stimulation protocols were applied in cyclic order.c, Slow afterpotential of the postsynaptic APs evoked by afferent stimulation (dotted trace) and current waveform injection (solid trace) and the pronounced afterhyperpolarization following an AP evoked by a rectangular current pulse (dashed trace) shown on an expanded voltage scale. The peaks of the APs are truncated. d, Comparison of the Ca2+ charge entering the soma during single APs, which were evoked using the three different stimulation protocols.