Fig. 5.
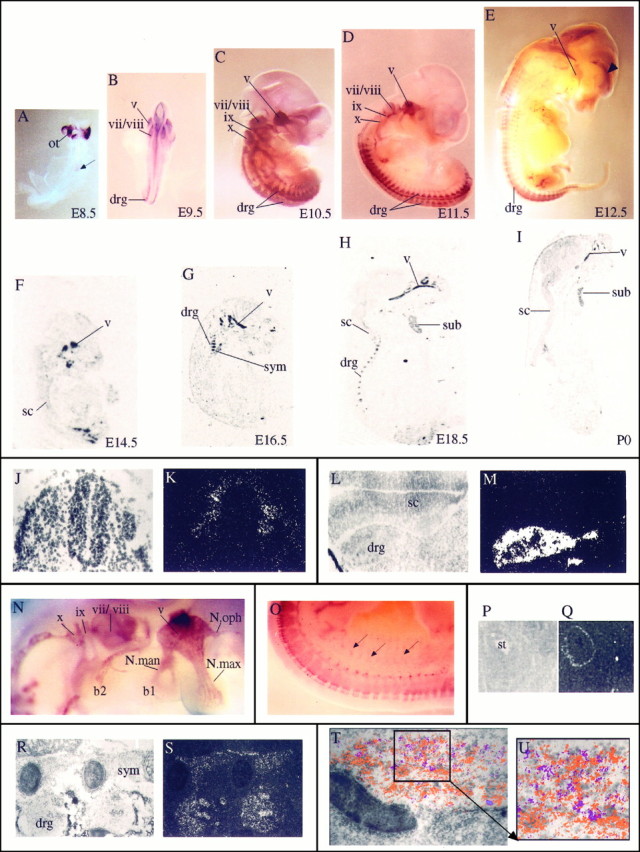
Localization of Sox10 transcripts in the developing PNS. A–I, In situhybridization of embryonic mice as whole mounts (A–E, from E8.5 to E12.5) or sagittal sections (F–I, from E14.5 to P0). A, B, Dorsal views; C–E, lateral views. The ventral surface in lateral views and sagittal sections is to the right; the dorsal surface is to theleft. Intense hybridization signals are detected over all ganglia and their corresponding nerve fibers. Thearrow in A marks the labeled cells in the already closed neural tube. The arrowhead inE points to a hybridization signal in the cortex, which was also seen with the sense probe but was never detected usingin situ hybridization on sections. Also note that no other hybridization signal was obtained with the sense probe. J, K, Corresponding bright- and dark-field photomicrographs of transverse section through E8.5 neural tube. L, M, Corresponding bright- and dark-field photomicrographs of cross-section through E11.5 spinal cord and the adjacent dorsal root ganglia.N, High magnification of the E11.5 embryo inD, showing hybridization over all facial–cranial ganglia and their fiber tracts. O, High magnification of the lower back region of the E12.5 embryo in E.Arrows point to some of the nerve fibers leaving the spinal cord area. P, Q, Corresponding bright- and dark-field photomicrographs of cross-section through the stomach of an E13.5 mouse. Transcripts were detected in the outer wall of the stomach. R, S, Corresponding bright- and dark-field photomicrographs of sagittal section through E16.5 sympathetic trunk and the dorsal root ganglia. T, Bright-field photomicrograph of E18.5 trigeminal ganglion with superimposed hybridization signals for Sox10 (orange) and SorLA (purple). Hybridization signals were obtained from dark-field images of adjacent sagittal sections and assigned false colors by computer imaging. U, Magnification of areaboxed in T. b1, Branchial arch 1; b2, branchial arch 2; drg, dorsal root ganglion; N.man, nervus mandibularis;N.max, nervus maxillaris; N.oph, nervus ophtalmicus; ot, otic vesicle; sc, spinal cord; st, stomach; sub, submandibulary gland; sym, sympathethic trunk. Cranial nerves and ganglia are in Roman numerals: v, trigeminal;vii, facial; viii, acoustic;ix, glossopharyngeal; x, vagus.
