Fig. 6.
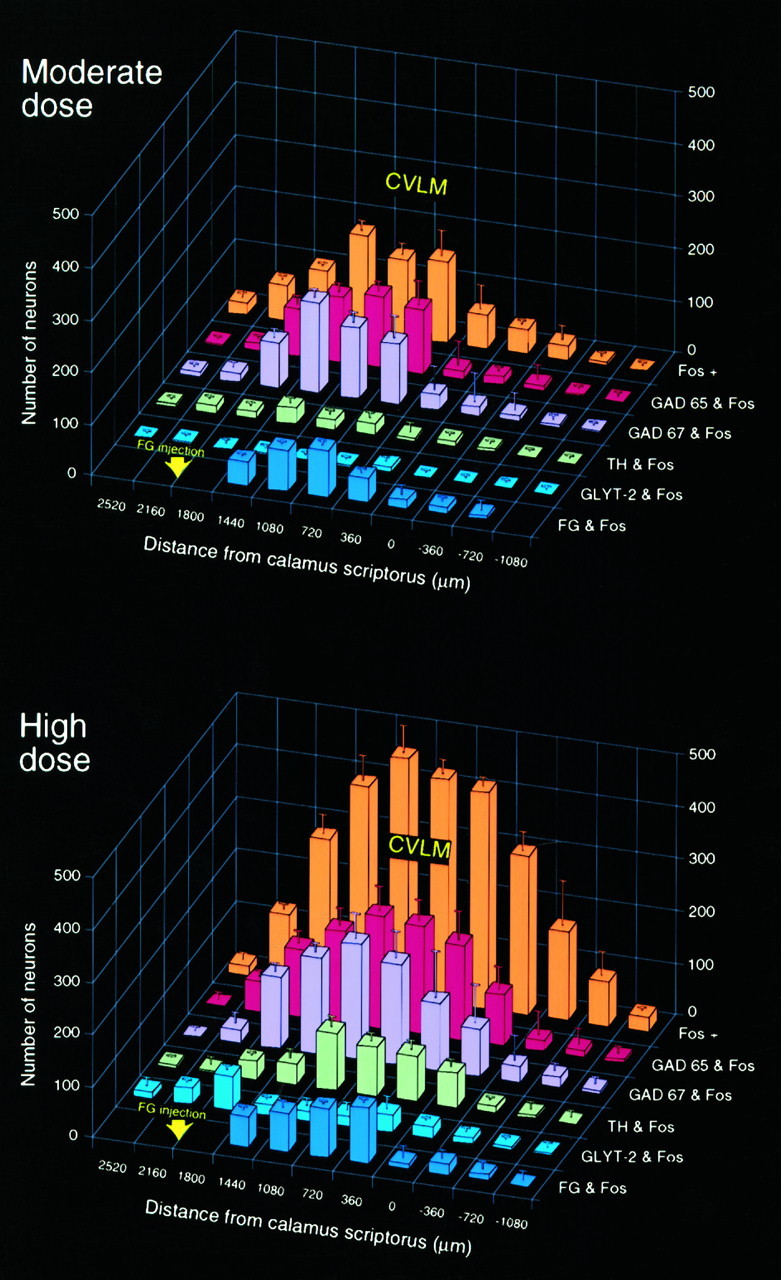
Anatomic and phenotypic characterization of PE-sensitive neurons of the VLM. A, B, Three-dimensional histograms showing the number of barosensitive (Fos-IR) neurons seen in response to moderate (A) and higher (B) doses of PE at regular intervals through the medulla (orange columns) and the number colabeled for GAD or GLYT-2 mRNAs, TH-IR, or a retrograde tracer (FG) after deposits in the RVLM at the level indicated. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 6–7/dose. Both PE doses induced c-fos expression concentrated between the level of the calamus scriptorius and that of the caudal aspect of the RVLM. In material from animals treated with a moderate PE dose, Fos-IR neurons were found to be predominantly GABAergic, with a majority projecting to the RVLM. A higher dose of PE gave rise to more robust Fos expression; a diminished proportion of these colabeled for GAD mRNA or the retrograde tracer, and an increased fraction displayed the catecholaminergic phenotype.
