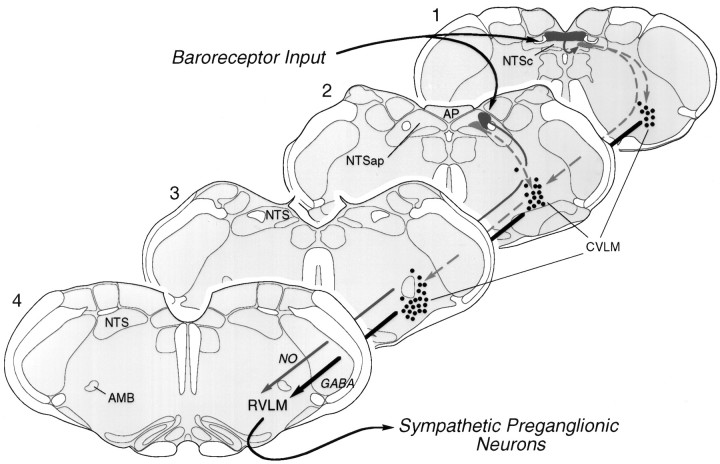
Fig. 9.
Summary of the organization of medullary baroreflex pathways. In the NTS, PE-induced Fos-IR is concentrated in a continuous strip (dark gray) occupying discrete aspects of the commissural and dorsal subnuclei at levels 1 and 2, respectively. We provide evidence here that a rostrally situated subset of barosensitive NTS neurons (level 2) projects directly to pressor sites in the RVLM (level 4) and/or expresses markers for the NO phenotype. Most barosensitive neurons of the NTS, however, do not project directly to the RVLM. The available evidence suggests that they come to influence sympathetic outflow indirectly, via one or more interneurons in the medial division of the NTS (light gray), which in turn projects to the CVLM (dashed lines). Based on criteria of phenotype and connectivity, we define the CVLM as a diffuse, longitudinally organized column of cells, maximally developed atlevel 3, and composed primarily of barosensitive neurons that are GABAergic neurons and project to the RVLM (thick black line). Drawings of sections through the medulla are modified from the atlas of Swanson (1992). AMB, Nucleus ambiguus;AP, area postrema; CVLM, caudal depressor region; NO, nitric oxide; NTS, nucleus of solitary tract; RVLM, rostral ventrolateral medulla;NTSap, NTS at the level of area postrema;NTSc, commissural NTS.