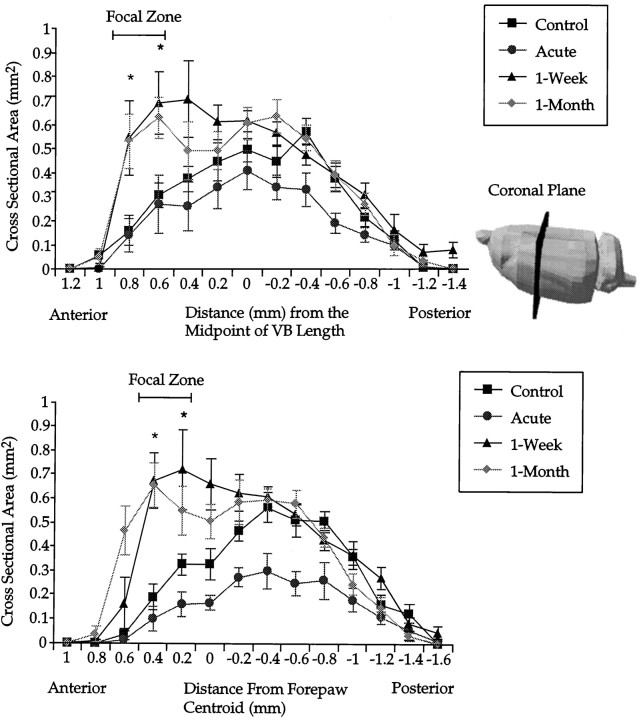
Fig. 3.
A, Coronal plane area of the shoulder sensory map as a function of anteroposterior distance. Maps from each animal are aligned with respect to the anatomically determined anteroposterior midpoint of the VB (anatomical registration). Lateral view of a rat brain indicates the plane of sectioning used on functional shoulder maps. The bar indicates a focal zone of robust change common to both 1 week and 1 month postlesion groups.Asterisks indicate that both 1 week and 1 month postlesion groups are significantly different from controls. Error bars indicate ±SE. B, Coronal plane area of the shoulder sensory map as a function of the anteroposterior distance. Maps from each animal are aligned with respect to the centroid of the forepaw (functional registration). Asterisks indicate that both 1 week and 1 month postlesioned groups are significantly different from controls. Compared with anatomical alignment of coronal slices (A), differences emerge more clearly with the functional alignment. All subsequent planar analysis is on coronal slices corresponding to the focal zone. Error bars indicate ±SE.