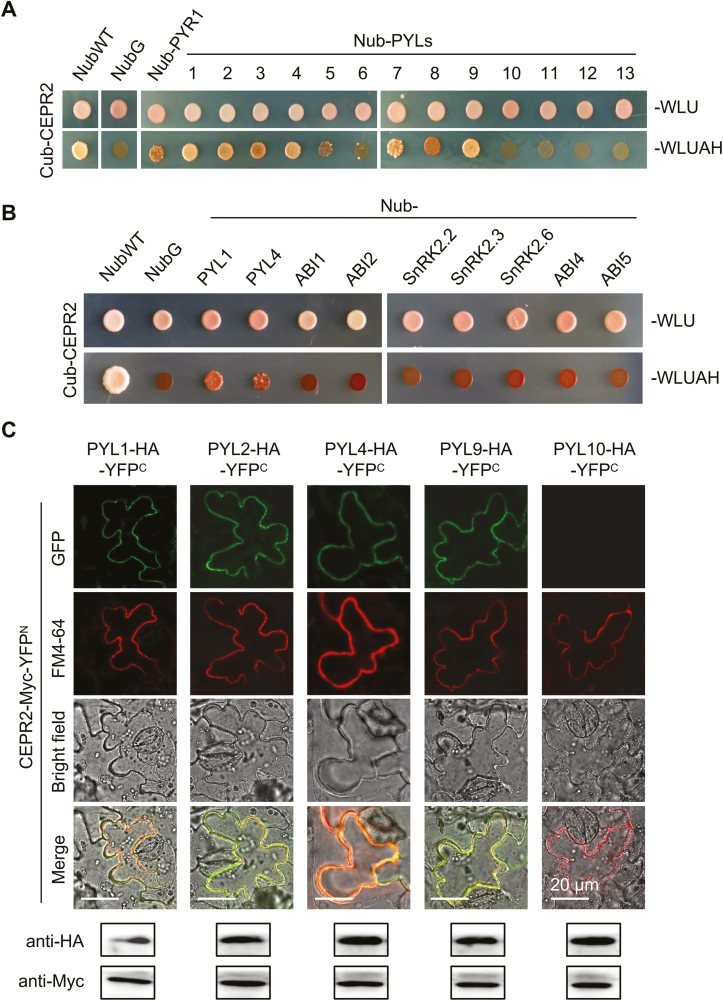
Fig. 1.
CEPR2 physically interacts with PYR/PYLs. (A) The MbSUS (mating-based split ubiquitin system) assay was performed to determine the interactions of CEPR2 with all members of PYLs. Images were taken after culturing at 30 °C for 4 d. ‘Cub-CEPR2 and NubWT’ were used as positive control, and ‘Cub-CEPR2 and NubG’ were used as negative control. (B) MbSUS assay showing the interactions of CEPR2 with other ABA signaling components. (C) The BiFC assay was performed in N. benthamiana to further confirm the interactions between CEPR2 and PYLs. Western blot assays were performed to verify whether CEPR2 and PYLs could be expressed in N. benthamiana. Anti-Myc antibody was used to examine the expression level of CEPR2, and anti-HA was used to examine the expression level of PYLs. PYL10, which does not interact with CEPR2 in the MbSUS assay, was used as a negative control. FM4-64 was used as a PM dye. FM4-64, N-(3-triethylammomiumpropyl) 4-(p-diethylaminophenylhexa-trienyl); PM, plasma membrane; BiFC, bimolecular fluorescence complementation. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)