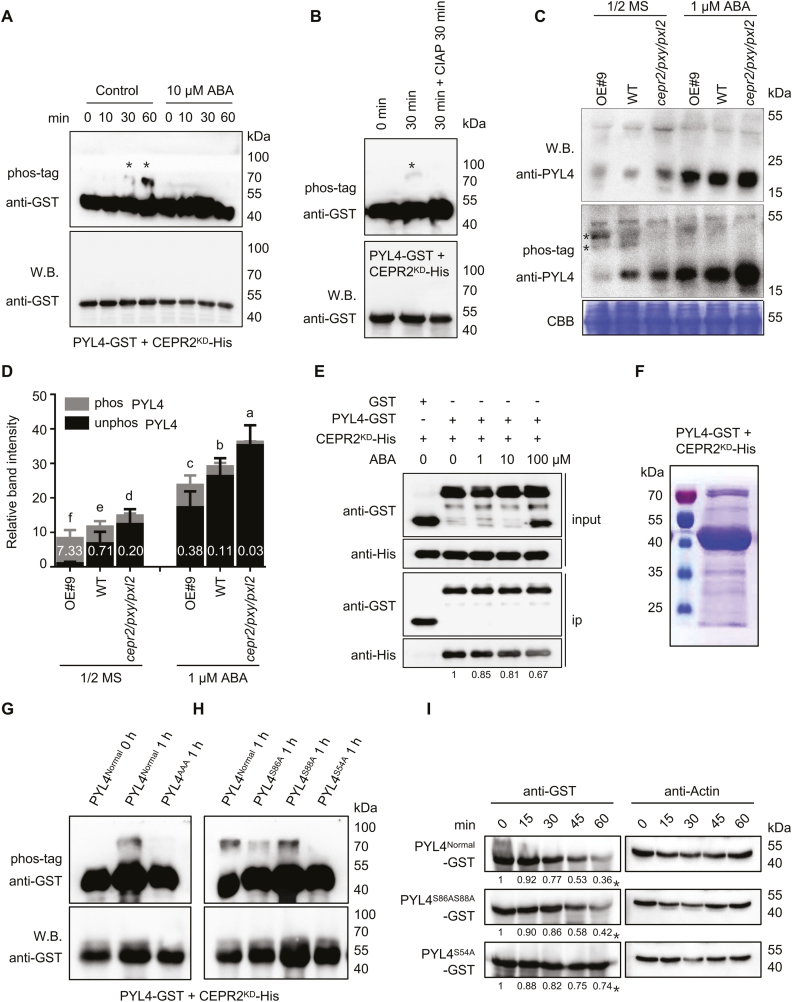
Fig. 5.
CEPR2 phosphorylates PYL4 in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vitro kinase assays showed that PYL4 was phosphorylated by CEPR2KD, while the phosphorylated PYL4 disappeared under ABA treatment. Western blot assay was used to detect the loading control and unphosphorylated PYL4. Phos-tag (50 µM) was used to isolate the phosphorylated forms of PYL4 in this kinase assay. The position of phosphorylated PYL4 is indicated by asterisks. (B) CIAP successfully removed the phosphoryl group of PYL4 in this kinase assay. CIAP, calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase, which is used to remove phosphate group(s) of proteins via dephosphorylation. (C) The phosphorylation levels of PYL4 in OE#9, WT, and cepr2/pxy/pxl2 seedlings grown on 1/2 MS or 1 µM ABA for 7 d were detected by anti-PYL4 antibody. Asterisks represent two different forms of phosphorylated PYL4, and the band above the arrows is a non-specific band. (D) The PYL4 protein levels shown in (C) were quantified by Image J. The phos PYL4/unphos PYL4 ratios were labeled in the columns in white. Error bars indicate the SE (n=3). P<0.05, one-way ANOVA. Statistical differences are indicated by lower case letters above the columns, and different letters represent different significance. (E) The pull-down assay showing the interaction of CEPR2KD-His and PYL4–GST with or without different concentrations of ABA. CEPR2KD-His was incubated with immobilized GST or PYL4–GST, and the proteins immunoprecipitated with GST beads were detected using anti-His antibody. (F) Phosphorylated PYL4 incubated in kinase buffer for 1 h was isolated by SDS–PAGE for phosphorylation site identification by MS. (G) All three serines identified by MS were artificially mutated into alanine (PYL4AAA), and the PYL4AAA protein completely lacked the ability to be phosphorylated by CEPR2KD in the in vitro kinase experiment. (H) Ser54, Ser86, and Ser88 of PYL4 were each artificially mutated into alanine, and only PYL4S54A completely lacked the ability to be phosphorylated by CEPR2KD in the in vitro kinase experiment. (I) A cell-free system was used to determine the degradation rate of PYL4 proteins in OE#9 lines. The protein levels of PYL4Normal–GST, PYL4S86AS88A–GST, and PYL4S54A–GST were detected by anti-GST antibody. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)