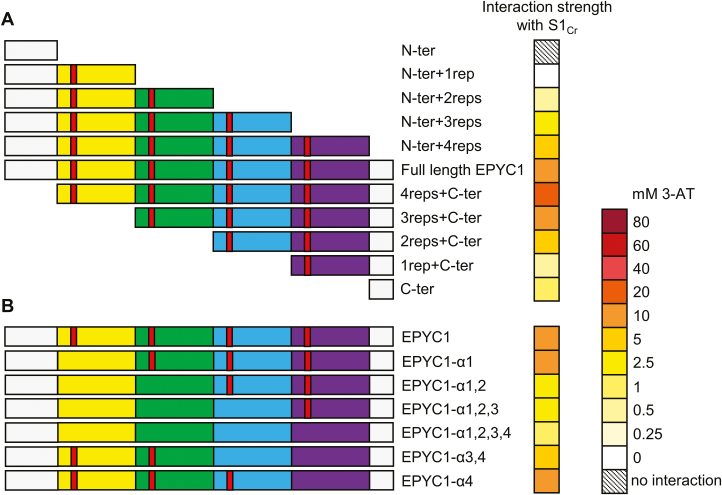
Fig. 3.
EPYC1 repeat regions contribute to interaction with the Rubisco small subunit. (A) Decreasing the number of EPYC1 repeat regions reduced the strength of interaction with S1Cr. (B) The predicted α-helical region in each repeat (red) is important for interaction with S1Cr. These were eliminated by matutation to seven alanines in each of the different EPYC1 variants. The heat map indicates interaction strength measured with yeast two-hybrid assays by the capacity for growth on increasing concentrations of 3-AT (mM). See Supplementary Fig. S3B and C for raw Y2H image data.