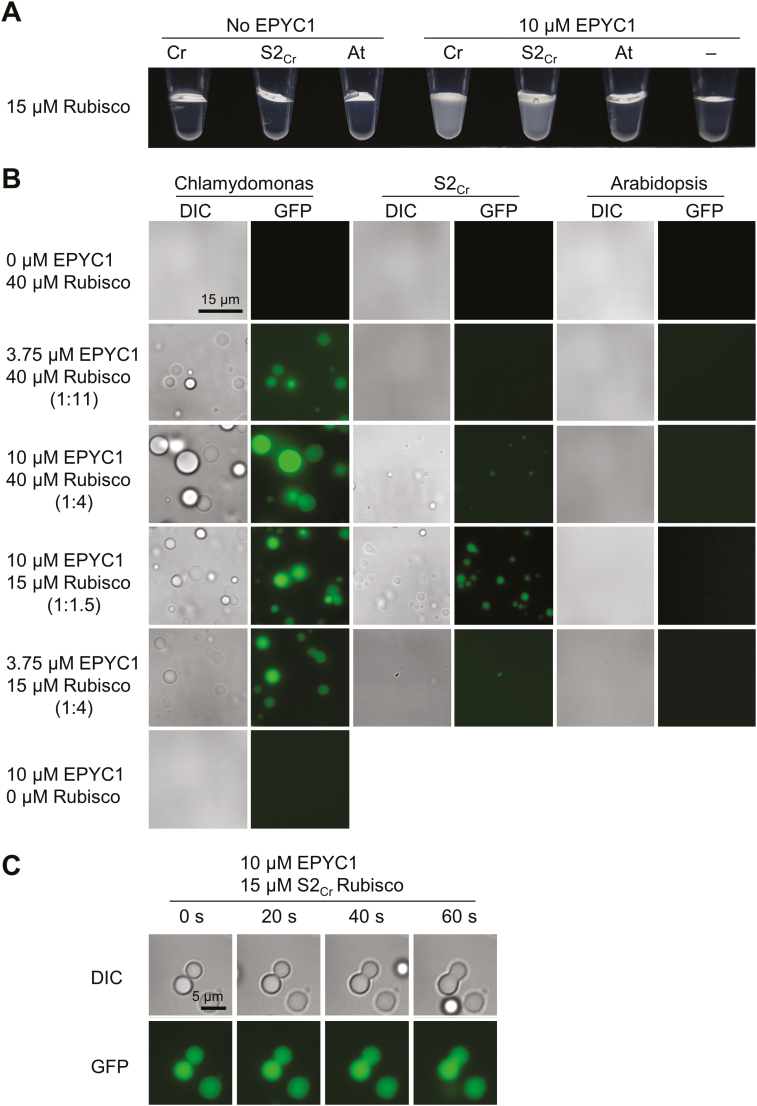
Fig. 8.
Hybrid Arabidopsis Rubisco carrying a Chlamydomonas small subunit is able to phase separate and form liquid droplets with EPYC1. (A) Addition of EPYC1 to Rubisco results in turbidity in Chlamydomonas (Cr) and hybrid (S2Cr), but not Arabidopsis (At) Rubisco (shown at ~3 min after mixing at room temperature). (B) The turbidity is caused by the formation of spherical droplets. Fluoresence in samples containing EPYC1 is due to the inclusion of EPYC1::GFP (0.25 µM). (C) Droplets from S2Cr Rubisco and EPYC1 fuse by coalescence. See Supplementary Fig. S11 for droplet sedimentation analysis.