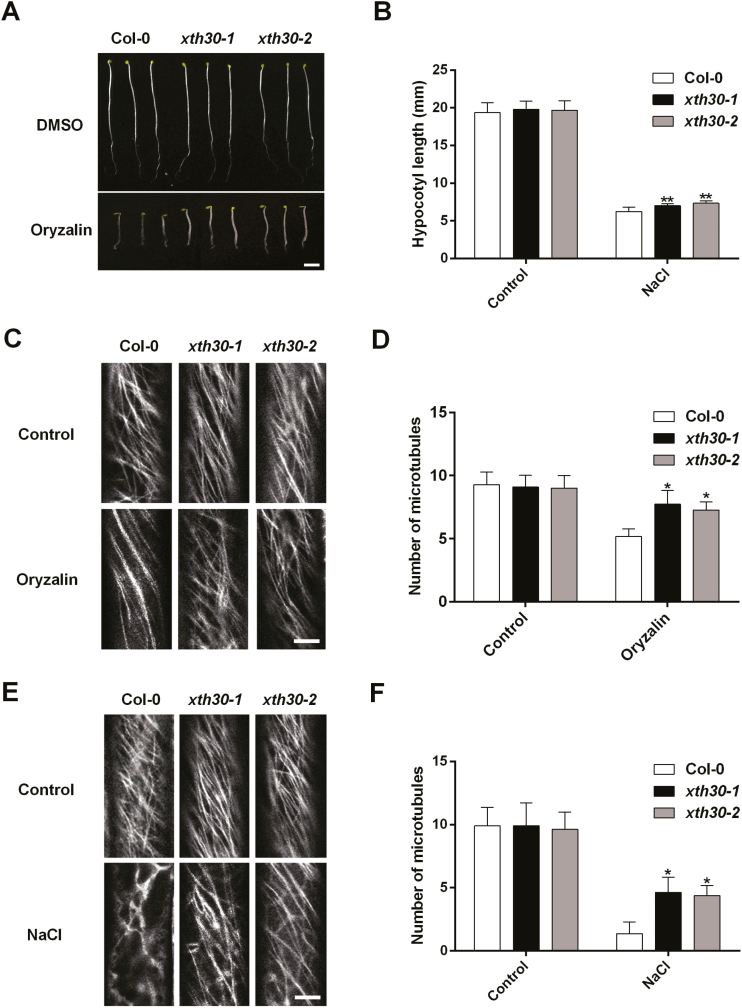
Fig. 7.
Knockout of XTH30 alleviates depolymerization of cortical microtubules under salt stress. (A) Seedlings germinated and grown for 6 d on 1/2 MS with or without 400 nM oryzalin in dark. (B) Quantification of hypocotyl elongation of seedlings in (A). Error bars represent SD, n>15 seedlings per biological replicate. Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. (C) Confocal images of GFP–TUA6 labeled cortical microtubules. Three-day-old etiolated seedlings were exposed to 10 µM oryzalin for 5 min. The epidermal cells in etiolated hypocotyls were observed. (D) Quantification of hypocotyl elongation of seedlings in (C). (E) Confocal images of GFP–TUA6 labeled cortical microtubules. Three-day-old etiolated seedlings were exposed to 100 mM NaCl for 12 h. The epidermal cells in etiolated hypocotyls were observed. (F) Quantification of hypocotyl elongation of seedlings in (E). The number of cortical microtubules in (D, F) was determined by counting the microtubules across a fixed line (~10 µm) vertical to the orientation of the most cortical microtubules of the cell. Data in (D, F) represent the mean ±SD of three independent experiments with a minimum of 10 cells from three seedlings assessed in each experiment. Scale bar in (A) indicates 3 mm, and scale bar in (C, E) indicates 5 μm. The asterisks in (B, D, F) indicate a significant difference between xth30 mutants and wild type using unpaired Student’s t-test (*P<0.05, **P<0.01).