Fig. 4.
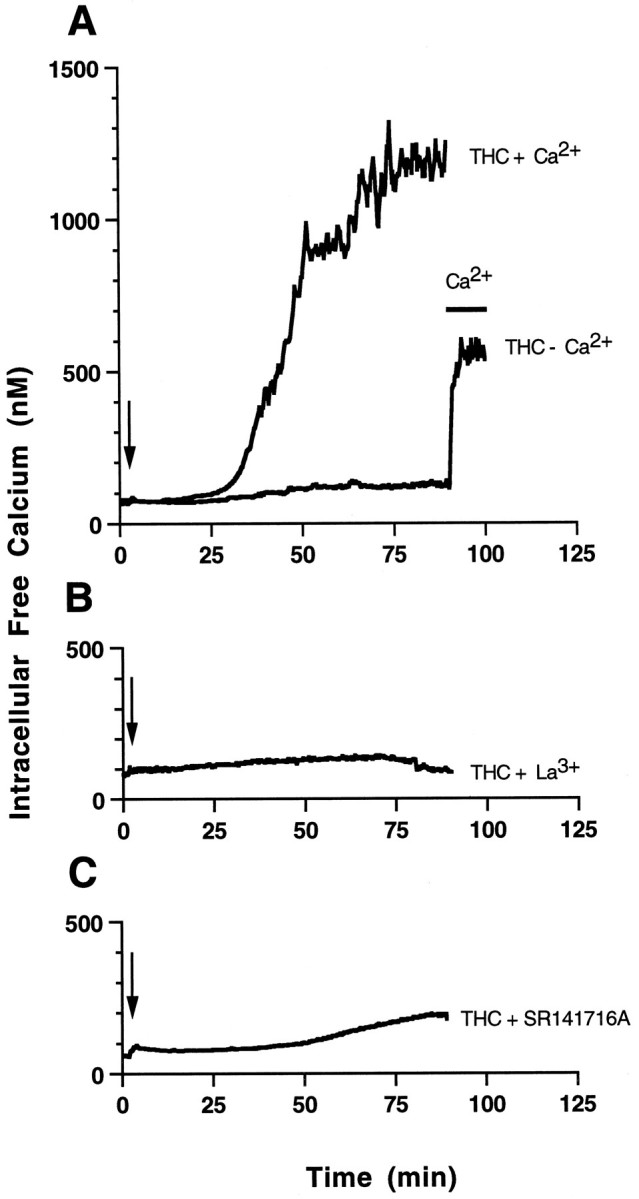
THC induces a delayed increase in intracellular Ca2+ that is dependent on extracellular Ca2+. [Ca2+]i of THC-treated primary hippocampal neurons was monitored by fura-2 fluorescent imaging. The calibrated [Ca2+]i (nm) was plotted against time (minutes). A, THC was added to neurons in the presence of 1.5 mm CaCl2 (THC + Ca2+) at the indicated time (arrow). No increase in intracellular Ca2+ was seen when the ethanol carrier (0.01%) was added alone (data not shown) or when THC was added to cells incubated without Ca2+ in the presence of 5 mm EGTA (THC − Ca2+). Four mm LaCl3(B) or 5 μm SR141716A (C) blocked increases in [Ca2+]i caused by 10 μmTHC.
