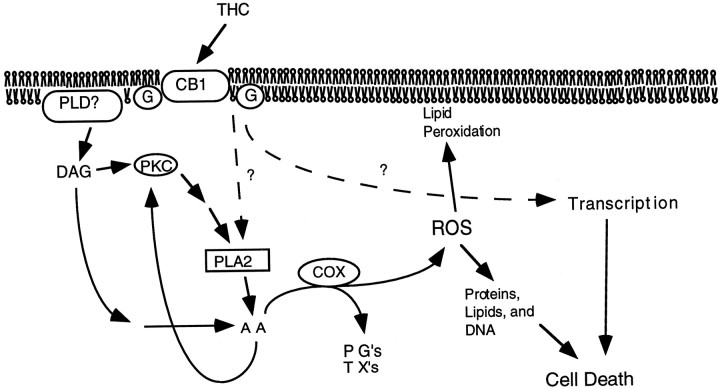
Fig. 9.
Signaling pathways contributing to THC-induced neuronal death. It is hypothesized that excessive stimulation of cannabinoid receptors (CB1) by THC stimulates the production of arachidonic acid (AA) by several pathways. Cyclooxygenase (COX) catalyzes the formation of prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which stimulates peroxidation of lipids, proteins, and DNA. In addition, cannabinoid-induced transcriptional events may also contribute to THC induction of neuron death.