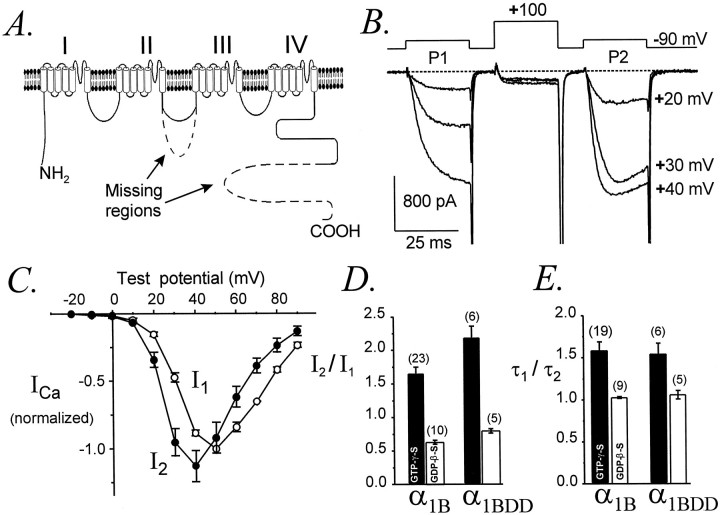
Fig. 11.
Undiminished G-protein-dependent modulation of α1B-DD. A, Diagrammatic representation of the mutant N-type Ca channel α1B-DD, which lacks amino acids 829–995 from the II–III loop and amino acids 1877–2338 from the C terminus. The deleted regions are indicated by dashed lines. B, Facilitation of α1B-DDcurrents, evoked using the standard voltage protocol. Data file 97321108; C = 43 pF; RS= 3.9 MΩ. C, Voltage dependence of inhibited (I1) and facilitated (I2) currents mediated by α1B-DD. I1 andI2 were normalized to the maximalI1 in each cell (n = 4). The standard voltage protocol was used. D, Facilitation of α1B-DD current amplitudes is slightly larger than for wild-type α1B. Standard voltage protocol, with P1 and P2 to +30 mV. The pipette contained GTPγS (filled bars) or GDPβS (unfilled bars).E, Facilitation of activation kinetics is identical for α1B-DD and α1B. With intracellular GTPγS, τ1/τ2 ratios were 1.60 ± 0.09 (n = 21) for α1B and 1.56 ± 0.11 (n = 6) for α1B-DD(p = 0.91). With intracellular GDPβS, τ1/τ2 ratios were 1.03 ± 0.01 (n = 5) for α1B and 1.06 ± 0.05 (n = 5) for α1B-DD(p = 0.41). D,E, Data from cells with maximal current densities of 15 ± 3 pA/pF (α1B,n = 23) and 18 ± 6 pA/pF (α1B-DD, n = 6) in the GTPγS experiments and 11 ± 5 pA/pF (α1B,n = 5) and 6 ± 1 pA/pF (α1B-DD, n = 5) in the GDPβS experiments.