Fig. 15.
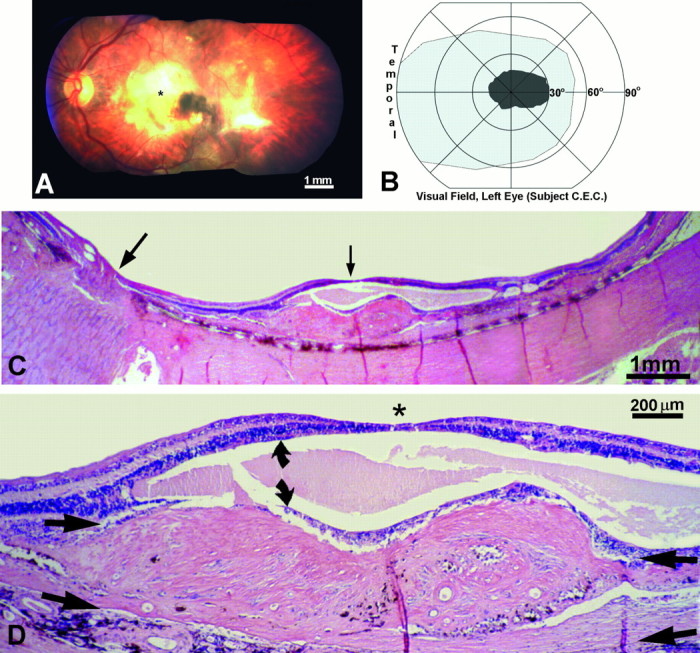
Human subject (C.E.C.). A, Left fundus, showing a macular scar (yellow area) from a fibrovascular membrane, which detached the retina locally and destroyed the photoreceptors. *Approximate location of the fovea.B, The macular scar caused a central scotoma, mapped on a Goldmann perimeter, which extended ∼30° into the nasal visual field. Within the scotoma the subject could not see a 1000 apostilb light spot 64 mm2 against a 31.5 apostilb background. C, Paraffin section cut along the horizontal meridian of the left retina, through the optic nerve (large arrow) and macula (small arrow), stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The retina was detached by a thick fibrovascular membrane. D, Magnified view, cut through the fovea (*), showing the fibrovascular membrane between the choroid and inner nuclear layer (arrow pairs). The photoreceptors were destroyed. The inner nuclear layer (curved arrows) was split by a large cyst, but the ganglion cell layer was relatively spared.
