Fig. 5.
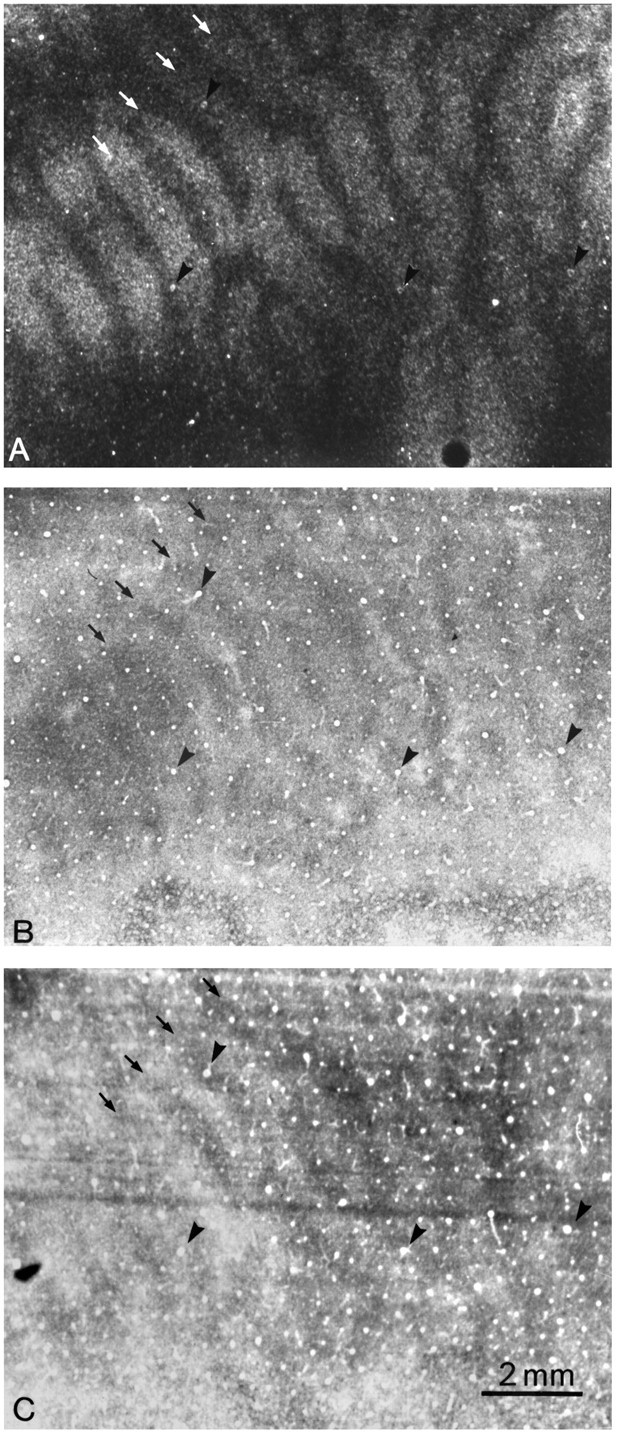
Monkey 4 (5 week monocular suture).A, Autoradiograph through the left operculum after injection of the left eye with [3H]proline at age 26 months, showing expanded ocular dominance columns (white arrows). The shrunken dark gaps correspond to the columns of the right eye, which was sutured at age 5 weeks. B, Adjacent section showing the characteristic CO suture pattern of thin dark columns alternating with wide pale columns. The thin dark columns (black arrows) are centered within the labeled ocular dominance columns in A but are much narrower. Their difference in width is made obvious by the fact that inA the proline-labeled columns are wider than the unlabeled columns, whereas inB the dark CO columns are narrower than the pale CO columns. C, Adjacent Luxol fast blue section showing dark columns (arrows), slightly wider than the corresponding columns in B. The presence of these columns suggests that cortical myelin content is altered by early visual deprivation. The complete column mosaic in this animal has been published (Horton and Hocking, 1997b, monkey 5).
